Ulrichsweb: Sample Searches -- Basic and Advanced
- Product: Ulrichs
What search features are available in the Ulrichsweb platform?
Ulrichsweb includes the following search modes: Basic Search and Advanced Search. Information about both modes, and examples of searches, are shown below.
Basic Search
The Basic Search feature is a single search box where you can enter titles, ISSNs, and keywords to find matching records. The default Boolean operation in Basic Search is OR, which means that you do not need to enter OR in the search box. The OR operation requires only one of the search terms to match in a record.
![]()
You can also use the following Boolean search operators:
-
AND – Both search terms must be found in a record.
-
NOT – The search term must not be found in a record.
The following example shows a basic search for the keywords music education. Results of this search include all records in which the words music or education are found in one or more of the fields indexed for Basic Search.
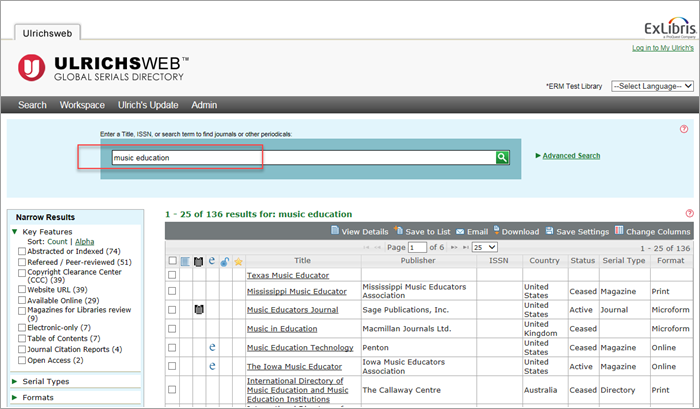
To begin a new search, you can either delete the contents of the Basic Search box and then enter your new terms or select the Search option from the main navigation bar.
Search Options
This section describes additional options that you can apply to searches within Ulrichsweb.
Wildcard Searches
You can expand your search terms using the following wildcard characters:
-
Asterisk (*) – Placing an asterisk within a word allows you to match zero or more characters at the position of the asterisk. For example, a search for ch*ter would match on words such as charter, character, and chapter. When used at the end of a word, such as music*, the asterisk wildcard will match on words such as music, musical, musicale, musician.
-
Question mark (?) – Placing a question mark within a word allows you to match a single character at the position of the question mark. For example, a search for modern? will match words such as modern, moderne, and moderna, but not for words such as modernization.
Wildcard characters cannot be used as the first character of a search.
Exact Title Searches
You can search for an exact title or phrase by enclosing search terms with quotations (such as “music education”). Ulrichsweb will find all titles that contain that exact phrase, without stemming your search words.
Proximity Searches
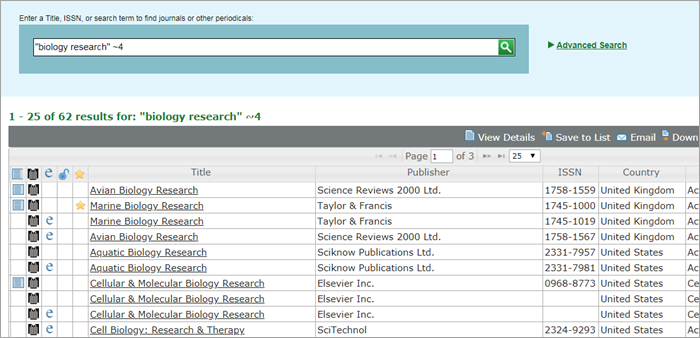
You can place a tilde and a numeric value (~<numeric_value>) after an exact title or phrase to define how close the search terms should appear to each other in a record. For example, the results for the proximity search “biology research”~4 includes only records in which the terms biology and research are four words apart or less.
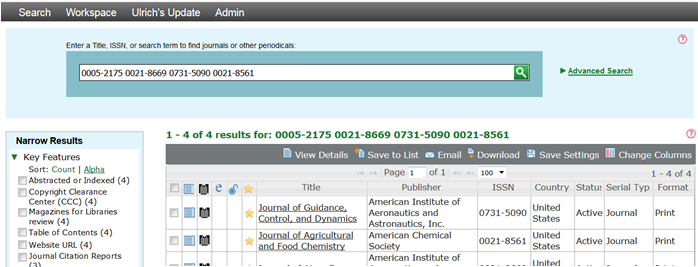
Search for Multiple ISSN
You can search for more than one ISSN at a time by separating each ISSN from the next with a space. The default Boolean operator OR will search for each ISSN individually and return records that contain any matched ISSN.
You may also search for multiple ISSN at a time by using the dedicated ISSN index in Advanced Search.
Facets
In the left navigation pane of the Search Results page, you can select facets to narrow your results by Key Features, Serial Types, Format, Content Types, Publication Status, Subject Areas, Publishers, Online Providers, and Edition Types.
Facets values can be expanded or collapsed using the triangle symbol next to the facet name.
In the following example, 51 of 136 search results are Refereed/Peer-reviewed. Select the check box and the search results to narrow the list to 51 items that are Refereed/Peer-Reviewed. Clear the check box to display the full list of 136 search results.
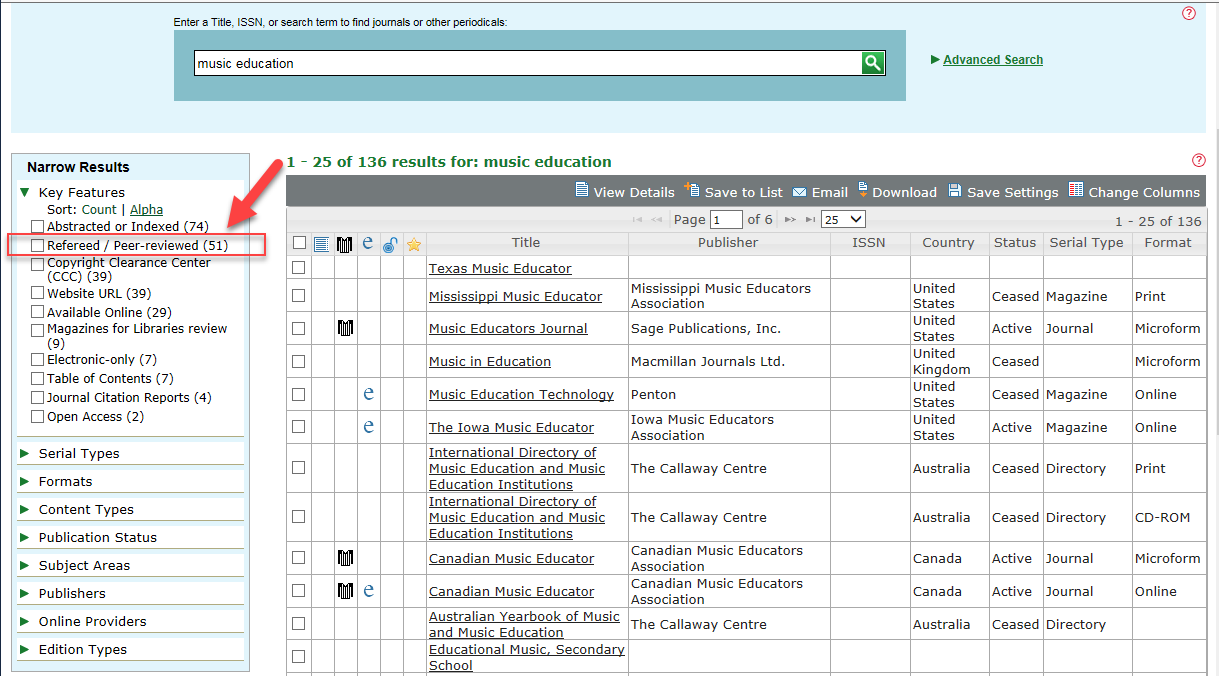
Results Toolbar
The Results Toolbar appears above the Search Results grid and indicates the actions you can take on your results.

-
View Details – You can click on any individual title to immediately view its title details. To view details for multiple titles, select their check boxes and then select the View Details option.
-
Save to List – You can save your search results to a temporary list of Marked Titles that is not retained between sessions, or to a user-defined List that is retained between sessions. A My Ulrich’s account is required to create user-defined Lists.
-
Email – You can email results to yourself or others from a user-defined List as either a PDF or a Text file in brief-record or full-record formats.
-
Download – You can export search results from a user-defined List as a PDF, Text, CSV or Excel file in brief-record or full-record formats.
-
Save Settings – If you have a My Ulrich’s account, you can save your preferred Change Columns search results displays for future sessions and update your preferences at any time.
-
Change Columns – You can temporarily add or remove columns from the Search Results grid during your current Ulrichsweb session. A My Ulrich’s account is not required for this action.
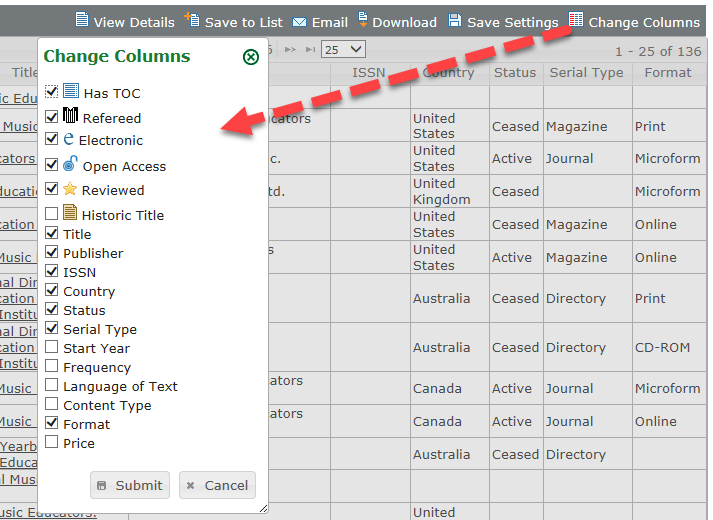 Change Columns Option
Change Columns Option
View Details
You can select either an individual title in search results or multiple titles and the View Details option to open the Title Details View, which displays all of the information about a title.
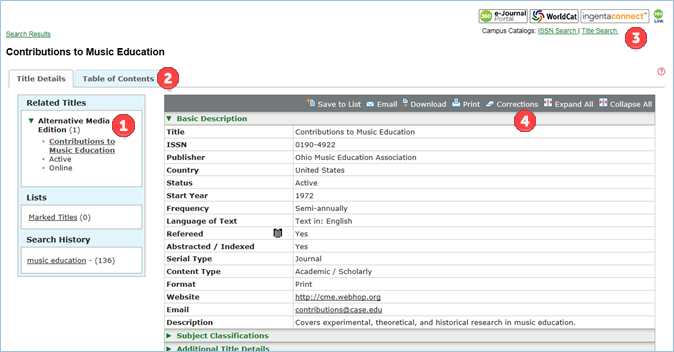
-
Related Titles – If other serials such as language or format editions or supplements are related to the title you are viewing, you can access information about them from the Title Details page.
-
Table of Contents – If present for a title, you will be able to browse tables of contents at the issue level, and search across all available issues by keyword. If you have enabled your OpenURL link resolver in the Ulrichsweb Administration Console, you will be able to search for full-text in your library’s electronic collection when you select a citation from the table of contents.
-
Linking Partners – You can set up title-level links to other services and your library catalog through the Ulrichsweb Administration Console. Linking partner icons or text you have configured will display.
-
Corrections – You can submit suggested corrections for any title directly to the Ulrich’s Content Operations team using the Corrections feature.
Advanced Search
The Advanced Search feature can be accessed from any Ulrichsweb page.
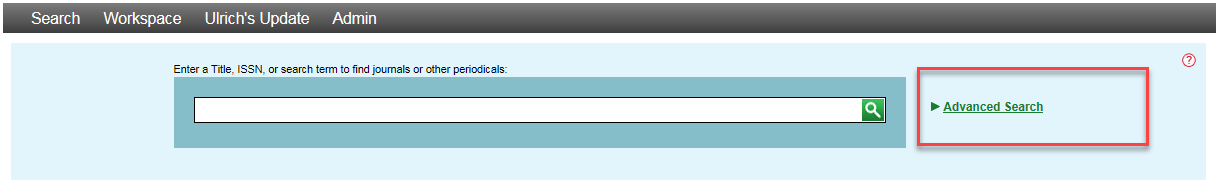
On the Advanced Search page, you can search using multiple indexes and limiters.
Use the Add Term, Match Search Terms, Add Group, and Match Search Groups options to build complex queries. Choose any of the Limiters you need to refine your search further.
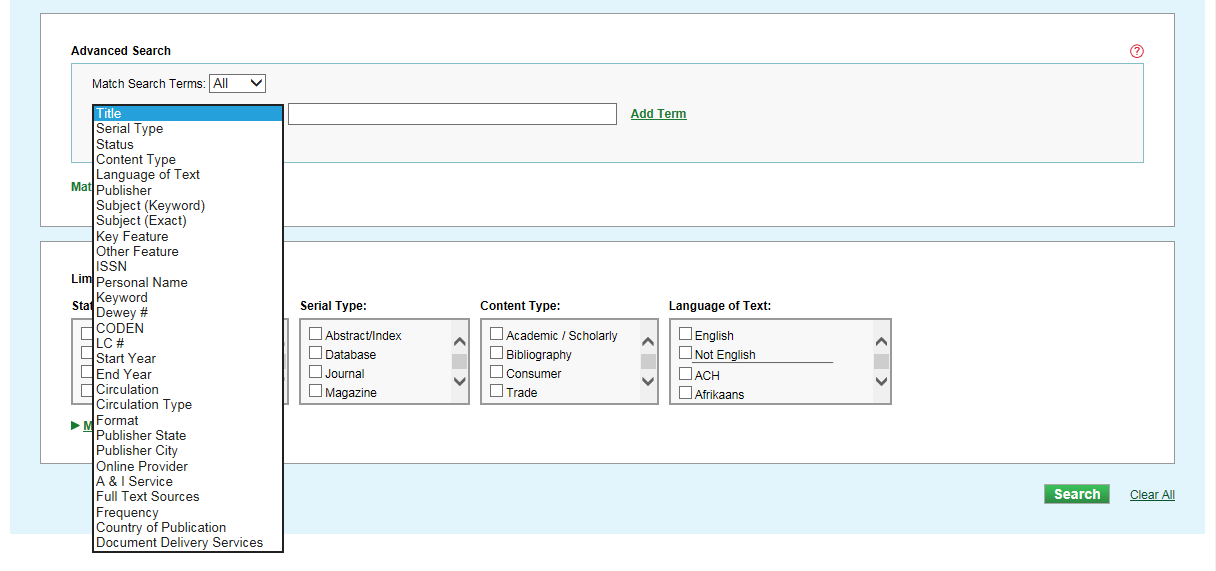
Your Advanced Search strategy will appear at the top of your search results, noting the options that you have specified.
Searching Individual Indexes
The default operation in Advanced Search indexes is OR, which requires only one of the specified terms to match in a record. For example, a Title search on music education will automatically search for the words music and education within a title, but only requiring one of the words to be found in a record.
To search an index for a phrase, enclose your search terms with quotation marks. For example, a Title search on “music education” (including the quotation marks) will automatically search for these words as a title phrase.
Some indexes, such as Key Feature, provide a drop-down list of controlled values that can be selected.
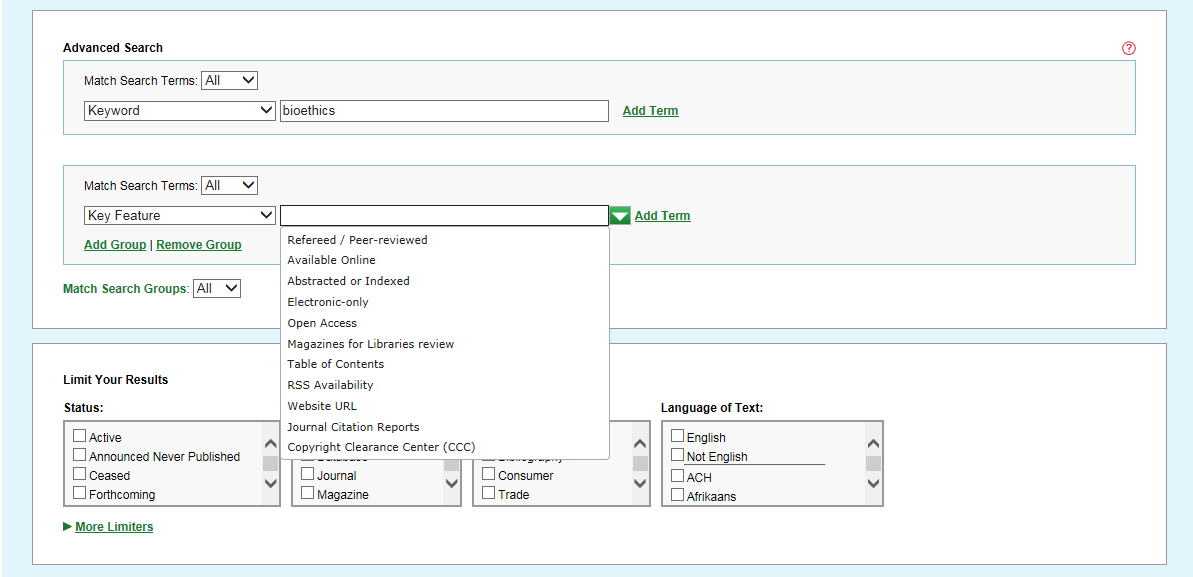
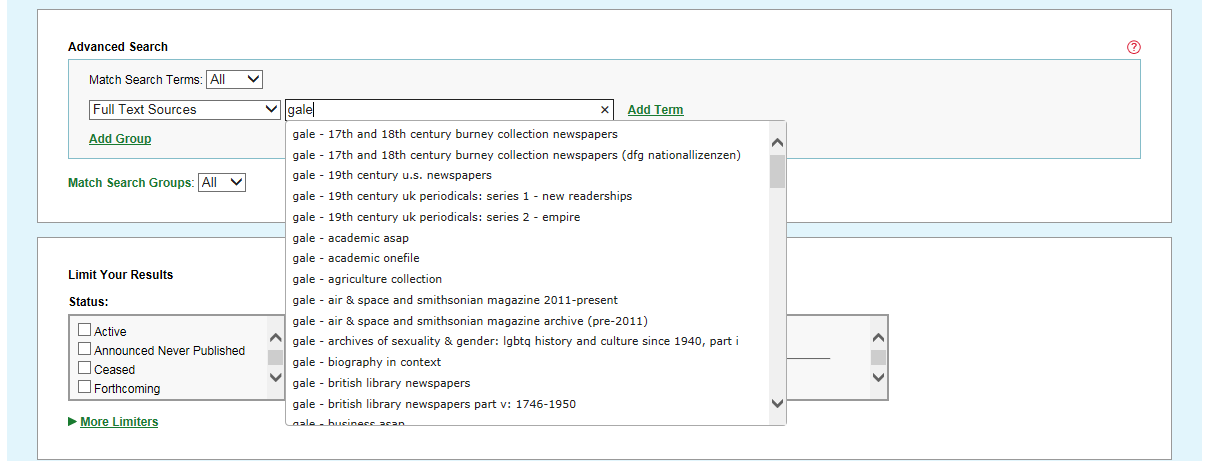
Other indexes, such as Publisher or A&I Service or Full Text Sources, provide dynamically-driven values that appear as you begin entering words.
For example, entering the provider’s name in the Full-Text Sources index box reveals a list of the provider’s online sources from which to select.
Add Term, Match Search Terms, Add Group, and Match Search Groups
When building an Advanced Search, the following options can be helpful.
-
Add Term – Adds a new row on which you can select another index from the drop-down list. The index you select may be the same index or a different index. Words in quotation marks within an index search box (for example, “music education”) or controlled vocabulary terms from auto-suggest indexes such as Key Feature or Publisher will be treated as a search phrase in that index. To remove a row, select Remove.
-
Match Search Terms – Controls the Boolean logic that combines the indexes you have selected.
-
All – requires a match on all of the rows; acts like the AND operator
-
Any – requires a match on any but not all of the rows; acts like the OR operator
-
None – requires a match on none of the rows; acts like the NOT operator
-
-
Add Group – Adds a new group to allow for nested Boolean searching. To remove a group, select Remove Group.
-
Match Search Groups – Controls the Boolean logic that combines the groups.
-
All – requires a match on all Groups; acts like the AND operator
-
Any – requires a match on any of the Groups; acts like the OR operator
-
You can further reduce the number of results by specifying additional criteria using Limiters.
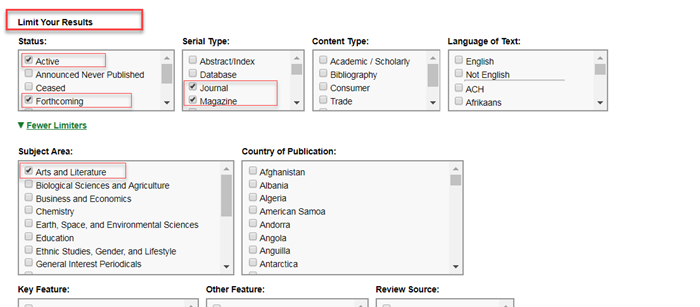
Using Limiters
When used with Advanced Search indexes, limiters help you reduce the number of search results in your query. Under Limit Your Results, you can display or hide limiters with More Limiters/Fewer Limiters.
Limiters can also be used by themselves to conduct a search. You can select multiple limiters and run your search without the need to use Advanced Search indexes.
-
The default Boolean operator within a Limiter group is OR, and you can select multiple limiters within a group.
-
Combining different groups of limiters conducts a Boolean AND search.
In the following example, the limiters are combined to search for records with a Status of either Active or Forthcoming, and a Serial Type of either Journal or Magazine, and the Subject Area of Arts and Literature.
Here are the results:
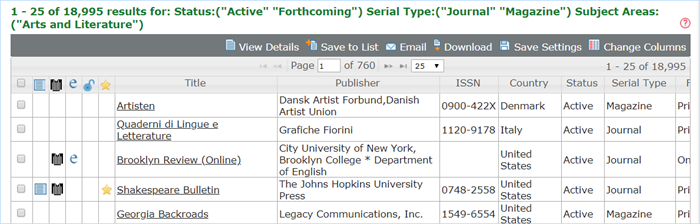
Sample Searches
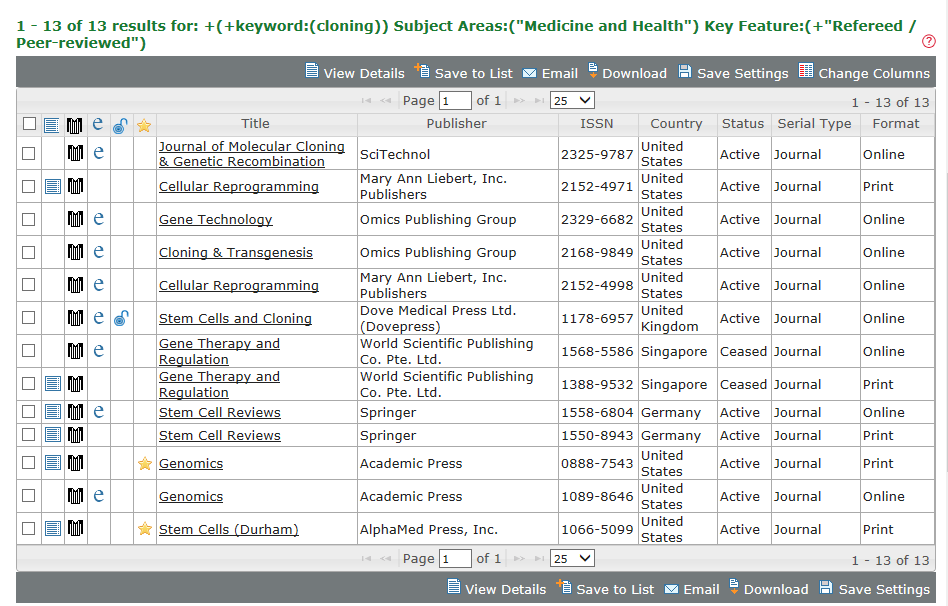
A simple Advanced Search might be to find publications using the term Cloning and limiting by the Refereed/Peer-reviewed Key Feature and the Medicine and Health Subject Area. The search criteria are displayed above the results:
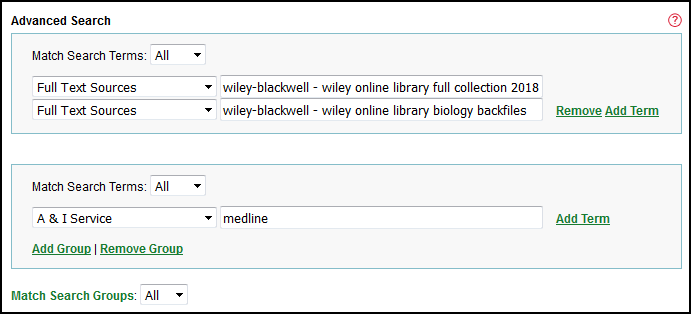
A more complex Advanced Search might compare title lists for two databases from the provider Wiley-Blackwell to identify titles in common between the databases and to require that the titles in common be indexed in a specific A&I Service: Medline.
Here is the strategy:
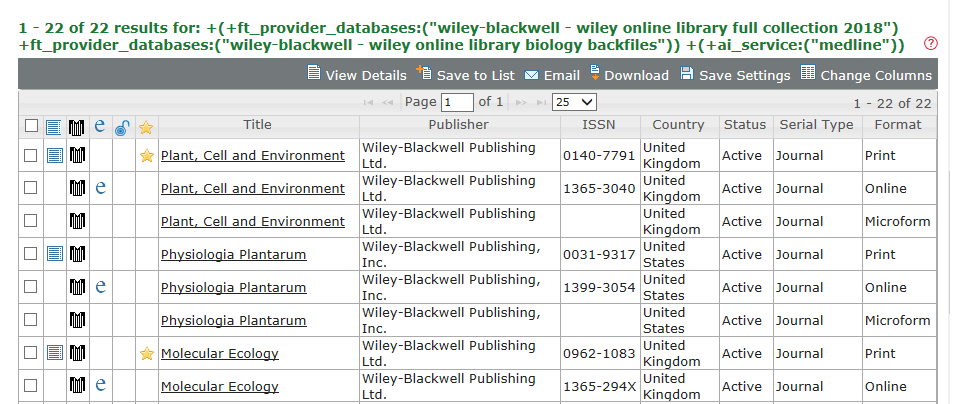
Here are the results, showing the search criteria used in the query:
For convenience, Ulrichsweb also displays search results and your Search History at the bottom of the Advanced Search page.
-
Date Created: 9-Feb-2014
-
Last Edited Date: 02-Aug-2018
-
Old Article Number: 8924

