Authentication
How does Alma authenticate patrons?
Alma can authenticate users using either a federated single-sign-on authentication system (for example based on the SAML 2.0 browser SSO Profile), or using a non-federated authentication. Currently, non-federated authentication options include an LDAP-based authentication.
To go into a bit more detail, A SAML (see below for other SSO options) Integration Profile may be configured in Alma. In this case, Alma does not actively authenticate users. Instead, it turns to the configured SAML system to verify the user’s identity.
Alma’s implementation of SSO is based on protocols such as the SAML (2.0) protocol. Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between security domains, that is, between an identity provider (a producer of assertions) and a service provider (a consumer of assertions). SAML is a product of the OASIS Security Services Technical Committee.
Alma utilizes the SAML protocol to communicate with any SAML-compliant system, enabling it to establish Single Sign On (SSO) with compliant systems, such as Shibboleth based systems, Microsoft Active Directory, and others that are SAML-compliant. This is illustrated below:
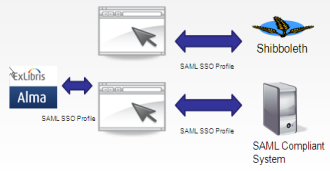
Alternatively, an LDAP Integration Profile may be configured in Alma. In this case, the authentication of any external user will be done by Alma using a secure protocol to directly communicate with the institutional LDAP server that is configured in the profile.
Fulfillment
Authentication is not necessary for on-campus users to be able to discover and access materials. For local materials, the library can choose which local collections can be made available to non-authenticated users. Users will only need to authenticate when placing a request, accessing a licensed full text resource, or when making use of their private space (e-shelf, saved queries, etc.).
Off-campus visitors can search and find results in Primo as configured by the library and according to agreements with the information providers. Any content in CDI that is restricted for search will not be discoverable or visible to an unauthenticated user. These materials include A&I databases. All other non-search restricted collections which the library chooses to activate in CDI are available to non-authenticated users.
What authentication mechanisms are supported?
Patron information is loaded into Alma from the institutional system and synchronized on a regular basis. It is possible to update an external user’s information manually in Alma, but these updates are overridden by the next synchronization with the user information system. Authentication of external users is performed outside of Alma—for example, in LDAP.
Alma supports Secured LDAP authentication with the local LDAP server that is used as the authenticating server for staff logins.
Alma’s authentication architecture supports single sign-on (SSO), which uses the enterprise identity provider authentication system. In this architecture, Alma delegates authentication to the customer's identity provider, whereby a circle of trust is built with the different domains. In this case (depending on the customer's identity provider being used), federation standards are applied.
Which identifier should be used for authentication?
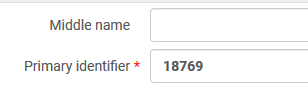
Ex Libris recommends using the Primary Identifier of the user record as the identifier for authentication.
What authentication schemes are supported?
Alma supports a number of authentication schemes, which are defined using Alma’s Integration Profiles. An institution may choose to use more than one. Supported authentication schemes include:
-
LDAP
-
SAML2 based authentication such as Shibboleth
-
OAuth based authentication with Facebook or Google
-
CAS
In addition, refer to the following link for more information - https://developers.exlibrisgroup.com/alma/integrations/user-management
Does Alma support Federated Single Sign On using Shibboleth version 3?
Yes, we can work with Shibboleth version 3 using SAML 2.0.
How does Alma manage authentication issues?
Alma’s management of authentication issues is managed in a number of ways, all of which are aligned with Ex Libris’ design goal of standardizing integrations with third-party systems while allowing for local fine tuning, using the Integration Profiles framework:
1. Based on a secure connection to the institutional LDAP or Central Authentication Service (CAS) system. When an access attempt is made, Alma sets up a direct secure link to the institutional LDAP server for obtaining access authorization.
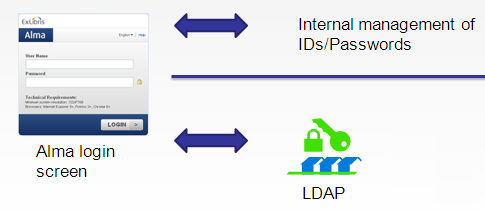
2. Based on federated SSO authentication using protocols such as SAML, CAS or OAuth.
Does Alma support standard authentication protocols?
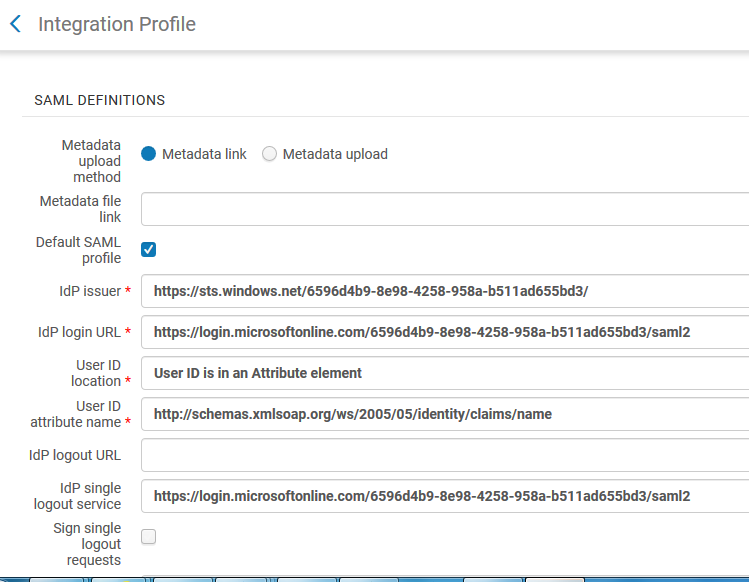
Alma’s authentication infrastructure makes use of integrations with identity providers systems, using standard protocols such as LDAP and SAML2. Integration with CAS in Alma is also supported, as well as OAuth authentication with Facebook or Google. The Alma integration is configured utilizing an Alma standard configuration element – the Integration Profile. Below is a sample Integration Profile for setting Alma integration with a SAML based IdP. Microsoft services, such as Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS2) and Unified Access Gateway (UAG) may be communicated with using SAML2. Shibboleth is also supported, if the institution’s Shibboleth implementation uses SAML 2.0.
Can there be multiple CAS profiles in a single institution?
A single institution may need to authenticate with two or more separate CAS IPs and can do so by creating multiple CAS integration profiles. This is achieved by defining a /cas/[profile code] suffix in the Alma URL. Alma uses the profile identified by the URL. When using a URL without the profile code in the suffix, Alma will use the CAS profile that is marked as the default.
Total views:
15480
