Administering the Solr Server
Administering the Solr Server
The Solr indexing mechanism uses a properties configuration table that is managed by Ex Libris and updated as needed with every release or service pack. All METS and DNX elements are indexed and searchable.
The Solr server also indexes all attributes, each of which has a corresponding row in the UI Labels code table. Customers can control the label of each indexed attribute through this table.
Index Rank
A new attribute added to the APPLICATION_VERSION table controls whether an index server (a server that has the IDX role) is active. Setting that attribute to one (1) means the index server is active and will be used by Solr for new/modified indexed information. Setting it to zero (0) means the index server will not be used by Solr for any new index rows. Modified index rows are still maintained in the same index server on which they were initially created.
Index Size and Location
The index size parameter, solr_server_capacity, defines the index size for all index servers. The value is defined in KB. Generally, for every 1 MB of files indexed, the system requires 2 GB of space.
The index size is informational only and not enforced by Rosetta. Index size is displayed in the Index Status UI and is also used to calculate the percentage of currently used index size.
The location of the index files is stored in the global properties file (for each server that is defined as IDX in its application role). The property name is dps.storage.idx. The default value is /exlibris/dps/d4_1/profile/solr/data.
Index Status
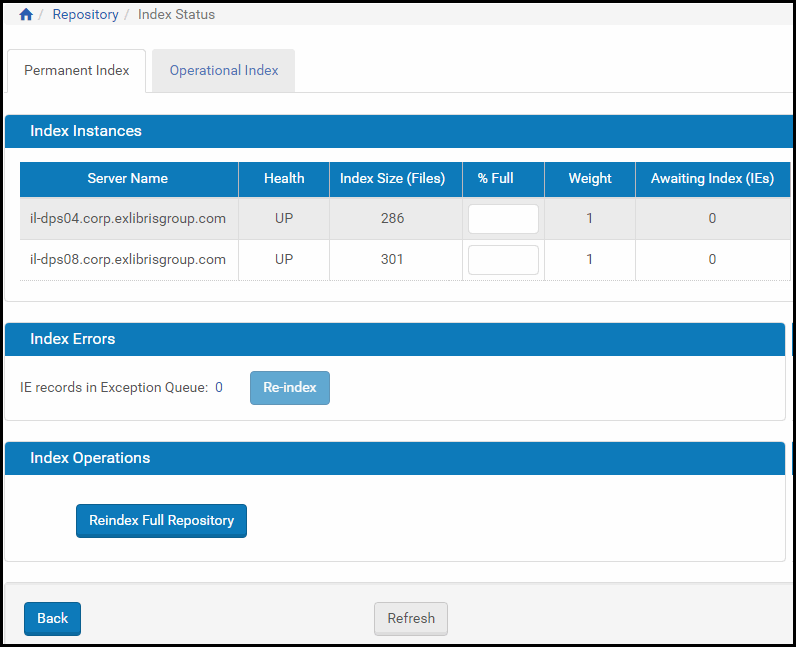
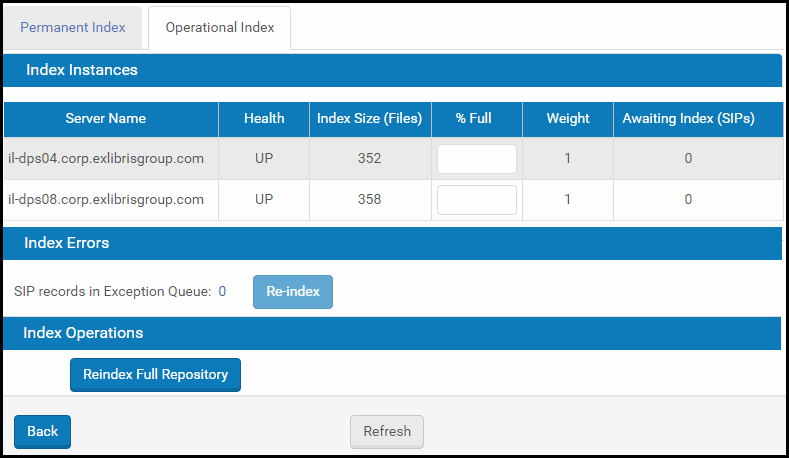
A page displaying the indexing progress is available from Administration > Repository Configuration > General > Index Status. The Permanent Index tab displays the indexing progress for IEs and the operational Index tab displays the indexing progress for SIPs.
Permanent Index Status Page from the Administration UI
Operational Index Status Page from the Administration UI
Details about Index Instances appear in the first section of the Index Status page. In the second section, Index Errors, the number of IEs/SIPs that failed during indexing, is shown. An option to resubmit the failed IEs/SIPs and re-activate the index process is also available in this section (Re-index button).
If there are records in the Exception Queue, clicking the number opens a list of the PIDs in the IEs/SIPs. These IEs/SIPs are not searchable by their metadata, but they can be reached by the quick search (using their PID).
You can run a full repository re-index from the third section of the page, Index Operations. A full re-index should be run in the following cases:
- New index fields or functionality requiring a global re-index
- Index corruption or hardware failure for an index node
- Addition or removal of an index node
Index Shards
When the SOLR index is managed on multiple servers, and one of the servers is down, the search results may not be returned from this server.
When this happens, objects that are indexedon that server are still available for delivery through a deep link URL (for example, from Primo).
In addition, searching IEs in Rosetta by PID works for all IEs, even the ones that are indexed on the server that is down.

