Working with the Rosetta System
Starting and Stopping the Rosetta Application Servers
This section explains how to start and stop the various Rosetta system servers.
To start/stop the Patron Directory Service (PDS):
- Log on to the PDS server.
- Run the following commands as user dps:
|
apcb apachectl stop apachectl start |
When running PDS on a port that requires root permissions (such as 80 or 443), the following command should be run (as root) to start/stop the service:
|
/exlibris/dps/d4_1/product/local/apache/bin/apachectl_auto /exlibris/dps/d4_1/product/local/apache/bin/apachectl stop |
To start/stop an application server:
- Log on to the server machine.
- Run the following commands:
|
dps_start dps_stop |
If there is more than one application server—either separate servers for Deposit, Staging, and Delivery, or in the case of a clustered environment (array of application servers managed by a load balancer)—these commands should be performed for each of the servers separately in the following order:
To shut down:
- Deposit
- Delivery
- Staging
- Permanent
To start up:
- Permanent
- Staging
- Delivery
- Deposit
If Rosetta is installed on a distributed environment (where each server can perform all roles—Deposit, Delivery, Staging, and so forth), there is no need to adhere to any shutdown/startup sequence.
To activate safe mode on the server:
While in safe mode no background jobs or processes (such as quartz jobs or queues) are running.
|
dps_start -s |
or
|
dps_start --safe |
To deactivate safe mode:
|
dps_start |
Verifying the Operation of the Rosetta System
After you have installed and configured your Rosetta system, verify that the system is working properly.
To verify that the system is working correctly:
- Log on to the Deposit Server at the following URL:
http://<Deposit Server machine>:1801/deposit - Log on to the Staging Server at the following URL:
http://<Staging Server machine>:1801/mng/wrk/ - Using the following URL, verify that the Permanent Server is up and running:
http://<Permanent Server machine>:1801/permanent/
Logging On to the Rosetta System
To enable Administrators to log on to the Rosetta system, one user with all administrative privileges is installed with the software. Administrators can use the following information to log on to the system:
- User name: admin1
- Password: For the default password, contact the Rosetta implementation/support teams.
- Institution code: INS01
After logging on, Administrators can begin initial configuration, which includes - changing their user name and password and
- adding new users.
You must change the password after the initial logon and setup.
System Checks
System checks are used to check essential components needed for running Rosetta properly.
| Name | Description (what is checked) | Action on warning/initial failure | Action on persisting failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBChecker | Application access to Oracle database | Rerun | Confirm Oracle is available |
| PDSCheckPlugin | Apache is running | Rerun | Restart Apache |
| PluginsCheckerPlugin | Plug-ins in plug-in directory are deployed/executable | Rerun | Check the plug-in directory is available and plug-ins have proper permission |
| SharedFoldersAccessChecker | Operational_shared is accessible (read and write) | Rerun | Fix permissions on operational_shared |
| SharedFoldersSpaceChecker | Operational_shared has at least 500MB free space | Rerun | Add space to operational_shared |
| StorageAccessChecker | All configured storage is accessible | Rerun | Mount storage to application server(s) |
| DepositWSChecker | Availability of web services | Rerun | Restart relevant server(s) |
| RepositoryWSChecker | |||
| PermanentWSChecker | |||
| DeliveryWSChecker | |||
| Storage Space Checker | Checks that the free space of all storage is not below the configured threshold. | Rerun | Add storage to the specified storage and configure storage definitions accordingly or free up space by deleting objects using Rosetta UI/APIs. |
Please contact Rosetta Support if you have difficulty resolving a failed system check.
Description of Aliases
The following table provides a list of aliases that are used by the system and in this guide.
| Alias | Description |
|---|---|
| dps_bin |
Shortcut to the Rosetta system’s bin directory
|
| dps_conf |
Shortcut to the Rosetta system’s configuration directory |
| dps_deploy | Shortcut to the Tomcat server’s web applications deploy directory |
| dps_log | Shortcut to the Rosetta server’s log directory |
| dps_util | Shortcut to the Oracle utilities |
| dps_start | Starts Rosetta |
| dps_stop | Stops Rosetta |
| pdsroot | Shortcut to the PDS directory |
| s+ [schema name] | Opens an SQL Plus session to the specified schema in Oracle |
| ver | Display basic information about the Rosetta environment |
| ver_full | Display extended information about the Rosetta environment |
PDS Directory Tree
Administrators can access the root directory of the Patron Directory Service (PDS) by entering the following command:
|
>>pdsroot |
In this directory, the following PDS subdirectories can be found:
- conf_table – Contains the main PDS tab_service.institute configuration files. Most of the PDS configurations are performed in this directory. These include LDAP configurations, attribute mapping file customizations, and so forth.
- program – Contains the PDS program files and modules
- html_form – Contains all of the HTML files used by the PDS, as well as customized versions of the various PDS screens
- service_proc – Contains internal PDS Perl routines used by the PDS for communication with various information sources
- pds_files – Stores all active session cookies
- pds_proc – Contains internal PDS utilities
Rosetta System Log Files
The Rosetta system automatically records process and event information in log files. All log files are stored in the log directory.
The table below describes the contents and locations of the log files in which the Rosetta system records this information:
| Log File | Contains | Location |
|---|---|---|
| server.log |
|
dps_log |
| pds_server.log | Information about internal interactions between the Rosetta system and Patron Directory Service (PDS) | /exlibris/dps/d4_1/log/ |
Rosetta server logs are automatically rotated and compressed. The following table describes Rosetta server.log rotation and compression naming convention policy:
| Event | Naming Convention | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Midnight | server.log.[datestamp].gz | |
| Server restart | server.log.[datestamp].[timestamp].gz | |
| Log file reaches 1 GB | server.log.1.gz, server.log.2.gz,... server.log.[n].gz | server.log.n.[datestamp].gz |
System, Background, and Operational Jobs
Rosetta runs the following types of jobs in the background:
- System – Jobs that are used for system maintenance and are not associated with a specific institution or workflow.
Only System Administrators can monitor and manage jobs of this type. - Background – Jobs of this type are configured to run frequently in order to maintain the smooth operation of Rosetta.
Only System Administrators can monitor and re-execute jobs of this type, but they cannot modify the job’s schedule. - Operational – Jobs that are associated with a specific institution or workflow and are managed by staff users in the Rosetta Management interface (such as submission jobs, the Risk Analysis Report job, and the Producer Report job).
System Administrators can only monitor jobs of this type.
The following table lists all the jobs that System Administrators can monitor with the Rosetta Administration interface. For more information, see Monitoring All Jobs.
| Job Name | Description | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Format Library Updates | Checks for (and installs) new available Format Library versions. Type: System Frequency: Every Sunday at 2:00 |
Install Automatically (false) |
| Analyze Retention Policy Deleted IEs Process | Evaluates IEs with retention policies to determine if they should be deleted. This job generates a table of IEs that is used for a report called IEs to be Deleted. Type: System Frequency: Every day at 2:00 |
|
| Delete IE By Retention Policy | Deletes IEs whose retention periods have expired. Type: System Frequency: Every day at 2:00 |
|
| Metadata Orphan Handler | Deletes unused CMS MD records. Type: System Frequency: Every day at 2:00 |
General Parameter: md_orphan_handler_interval_in_second |
| Index Optimize | IDX00 Oracle text index optimize Type: System Frequency: Every day at 2:00 |
|
| Startup Checks Job | Startup checks are used to check essential components needed for running Rosetta properly. Type: System |
|
| Metadata Loader | Aleph/Voyager updates Type: System Frequency: Every two hours |
General Parameter: md_load_interval_in_second |
| Statistics Analyzer | Gather event statistics Type: System Frequency: Every 15 minutes |
General Parameter: statistic_interval |
| Plan Execution Monitor | Preservation Processing Type: System Frequency: Every five seconds |
|
| Storage Integrity | Searches for missing and orphaned files. Works with the NFS and S3 Storage Plugins. Type: System |
|
| Submission | Bulk submission jobs that are created and managed by Preservation Managers and Analysts in the Rosetta Management interface. Type: Operational |
|
| OAI-PMH Harvester | Type: Operational | |
| Risk Report | Generates the Risk Analysis report at an institutional level. Type: Operational |
|
| Producer Report | Generates and emails the report of producer deposits at an institutional level. Type: Operational |
|
| Find Duplicates | Finds duplicates across the repository. Type: System Frequency: Do not run |
Email distribution Maximum number of duplicates to be reported can be configured. |
| Clean Up | Removes old data from the file system and the database. Type: System Frequency: Every Sunday at 1:00 |
Data older than x days. Can be configured separately for different areas. Enter 0 for Clean Old Deposit Jobs and Clean Finished SIPs to clean all jobs or SIPs.
When selecting Clean Deleted OAI-PMH records, it is recommended that you set the OAI deletedRecord policy to transient in the oaiproviderconfig.xml configuration file.
Clean Old Events can be configured to include/exclude specific event types. |
| DepIndex Optimize | Indexes the deposit tables so that they can be searched by the system and users. Type: Background Frequency: Every day at 2:00 |
|
| Index Synch | Makes sure that each new object (IE) is indexed so that it can be searched in the system. Type: System Frequency: Every one minute |
|
| Process Automation Monitor | Process Execution Type: System Frequency: Every five seconds |
|
| Delete Deposits | Deletes deposit directories (parent defined under general parameter logic_deposit_area) for deposits that were declined or deleted. Type: Background Frequency: Every Sunday at 1:00 |
|
| Refresh Materialized Views Job | Refresh the data needed for the Formats Breakdown report Type: Operational Frequency: Daily at 3:00 |
Monitoring All Jobs
The Manage Scheduled Jobs page enables System Administrators to monitor the status of all jobs. To access this page, click Manage Scheduled Jobs on the Administration page.
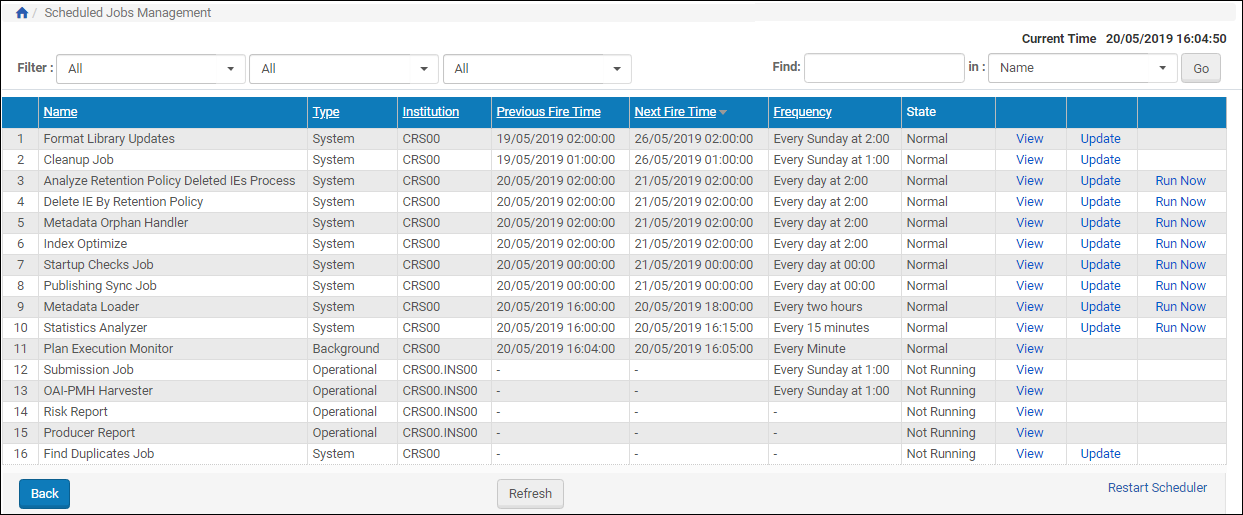
Manage Scheduled Jobs
Depending on the type of job, System Administrators can perform the following tasks from this page:
- View a job’s details – Click the View link next to the job you want to view.
- Schedule a job – For more information, see Scheduling a System Job.
- Execute a job – Click the Run Now link to run a job manually.
In addition, System Administrators can cancel a system job. For more information, see Canceling a System Job.
Scheduling a System Job
This task allows System Administrators to schedule a system job.
To schedule a system job:
- On the Manage Scheduled Jobs page, click the Edit link next to the job that you want to modify.
The Job Details page opens.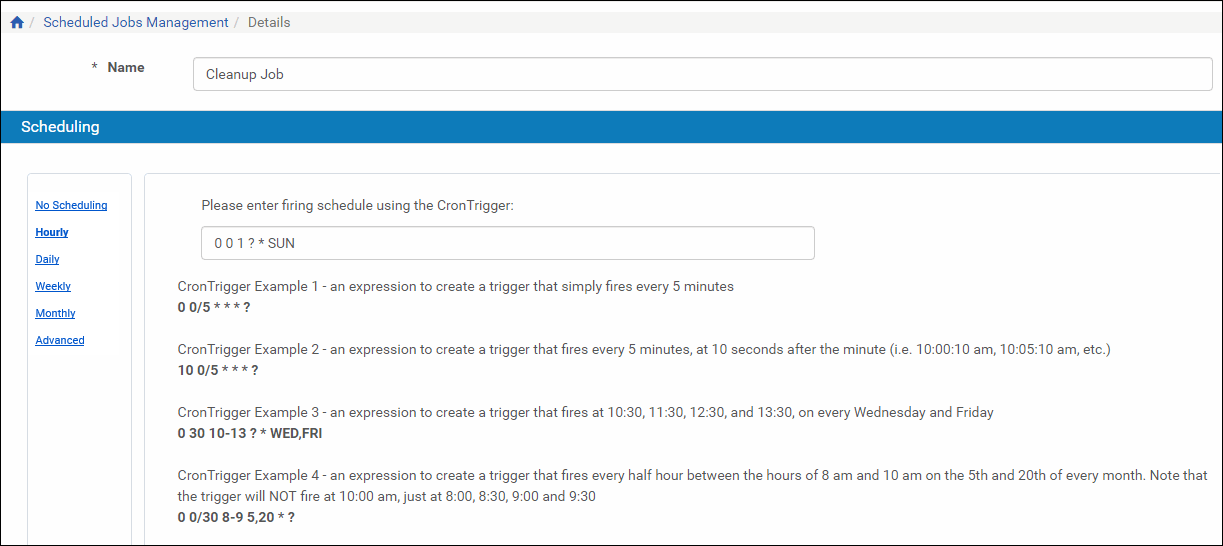 Job Details Page
Job Details Page - Select the interval at which to execute the job: No Scheduling, Hourly, Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or Advanced.
- To configure hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly intervals:
- Use the following table to configure the common interval fields:
Common Interval Fields Section Field Description Start At Time Select the hour and minutes from the drop-down fields to specify the time at which to run the job. Date Use the calendar tool or select the month, day, and year from the drop-down fields to select the date at which to start running the job. Repeat Indefinitely Select this option to run the job indefinitely. Until Select the month, day, and year from the drop-down fields to specify the date at which to stop running the job. After this date, the state of the job will change from Normal to Not Running. - Use the following table to configure the interval-specific fields:
Interval-Specific Fields Type of Interval Perform this task: Description Hourly Every Select the hourly interval from the Hours drop-down field. Weekly Week days Select which days of the week to run this job. Monthly Monthly At Select the day of the month to run this job. For information on how to configure advanced intervals, see section Configuring Advanced Schedules in the Rosetta Staff User’s Guide.
- Use the following table to configure the common interval fields:
- Click the Apply button to add the job to the list of submission jobs.
Canceling a System Job
Canceling a system job allows the System Administrator to postpone the execution of the job indefinitely without deleting it from the system.
The Unschedule option will not be available when the state of the job is Not Running.
To cancel a system job:
- On the Manage Scheduled Jobs page, click the Edit link next to the job that you want to modify.
The Job Details page opens. - Click the Unschedule button.
The state of the job should change to Not Running.
Shared Directories
Rosetta needs access to several mount points and shared directories in order to operate. The mount points are defined in the Operational Repository and the Permanent Repository. They can be found in the Storage Rules and Definitions area under Administration > Repository Configuration.
For the deposit area (where the deposited files are initially stored) and for the operational shared objects (such as plug-ins and temporary folders), the mount point is defined in the General Parameters table (found in Administration > System Configuration > General > General Parameters).
Operational and Permanent Repository Definitions
Both the Operational Repository and Permanent Repository are defined in Storage Definitions. For new installations, a mount point is assigned for each repository, and the out-of-the-box values are replaced with the values provided during installation through RosiKit.
Deposit Area
The deposit area is defined by the logic_deposit_area general parameter in the Deposit module.
Operational Shared
There is a single operational shared directory which must be shared among all servers. It is defined by the operational_shared general parameter in the General module. Under that folder, the following directories are defined and used by the system.
| Name | Module | Location | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| operational_delivery_shared | Delivery | operational_shared/operational_delivery_shared/ | Hold Delivery file cache, Delivery UI skins |
| plugin_directory | General | operational_shared/plugins | Root folder for plug-ins |
| plugin_deploy_jar_dir | General | operational_shared/plugins/deploy | Holds plug-in .jar files |
| plugin_deploy_script_dir | General | operational_shared/plugins/bin | Holds plug-in scripts |
| preservation_export_directory | Backoffice | operational_shared/operational_export_directory | Holds import and export representations during preservation test/action |
| convert_temp_directory | Repository | operational_shared/operational_delivery_shared/convert_temp/ | Used by converter script (thumbnail, jpeg2000) |
| sip_temp_directory | Repository | operational_shared/sipTmpDir/ | Used by converter script (thumbnail, jpeg2000) |
| bytestream_working_dir | Repository | operational_shared/bytestream_work | Used for creation of bytestreams |
| NamedFolders (Mapping Table) | Delivery | operational_shared/operational_delivery_shared/work/jmagick/ | JMajick work directory; Only required when Operational and Delivery servers are separate |
| digital_certificate | General | operational_shared/DigitalPreservationSystem.pfx | Location for email-signing certificate |
| staff_work_area_directory | Backoffice | operational_shared/staff_work_area/[user-name] | Location used by staff users for export/import |
| preserve_pp_docs | Backoffice | operational_shared/preserve_pp_docs | Location that signed-off preservation plans are exported to. A submission job can be configured to ingest exports from this location. |

