The AI Metadata Assistant in the Metadata Editor
What is the AI Metadata Assistant
The AI Metadata Assistant uses a Large Language Model generative AI to process information about a library resource, and suggest relevant metadata to the cataloger to help make the cataloging process quicker and more efficient. The cataloger can then review the suggested data and accept, correct or dismiss it, as well as add more complex, expert metadata and library-specific metadata.
The AI Metadata Assistant can process images of a library resource along with other provided information, extract the text and meaning, and return it structured according to cataloging standards. It can be used for creating new bibliographic records, as well as enriching existing brief records.
Phase I
Phase I of Alma’s AI Metadata Assistant supports creating and enriching MARC 21 records in the English language – more cataloging and resource languages and formats are added in future phases, as we work with the community to evaluate the AI’s capabilities and quality of metadata.
The subjects provided are validated against Library of Congress vocabularies, with plans to increase the selection of authority vocabularies in future phases.
Future Plans
Future phases plans include support for more languages, authority vocabularies and cataloging formats.
We are working with various libraries around the world to assess usability and metadata quality for:
- More languages, subject vocabularies and cataloging formats.
- Bulk record enrichment processes
- Bulk record creation processes
We are also exploring options for bulk processes – assessing what metadata, and in which scenarios and workflows, would be useful for libraries.
Capabilities and Limitations
This service applies generative AI, which may result in limitations, inaccuracies, or biases in the output – the mediated workflow combines the AI capabilities with the librarian’s expertise to balance efficiency and accuracy.
Large Language Model generative AI tools are agile, and their responses differ between uses and evolve over time. We are continually working with the community to maximize the usefulness and accuracy of the returned data, and to maintain the efficiency of our prompts and data processing.
However, while we phrase our prompts carefully, there are cases where the AI:
- Returns inaccurate or generic data (e.g. irrelevant edition information).
- Doesn’t accurately follow cataloging standards as an expert cataloger would (e.g. missing ISBD punctuation or using wrong MARC field indicators).
- Doesn’t return all requested metadata fields.
- Is not accurately processing some languages when cataloging resources in those languages.
- Does not return correct subjects for certain authority vocabularies.
- Cannot always process images in certain conditions, such as poor image quality, a lot of noise in the image background, or if the image is not upright.
What We’re Doing to Mitigate These Limitations
-
Working with catalogers and the Alma community to assess the metadata quality and improve it.
-
Validating returned subjects against authority files: We check that the returned subject matches an existing authority record, and link to it either fully or partially. It may match either the preferred or non-preferred term, if a non-preferred term is suggested by the AI, it can be updated to the preferred term either by the cataloger, using F3 in the Metadata Editor, or automatically by the scheduled "Authorities - Preferred Term Correction" job (for more information see Jobs Related to Authority Records).
-
Adding gradual support for different languages and vocabularies, in cooperation with libraries working in them and according to the AI model’s growing capabilities.
-
Applying normalization processes to format and clean up data, as well as add data provenance information.
-
Monitoring catalogers' feedback and updating our prompts periodically using a new scheduled job, Synchronize AI settings.
-
Developing tools for libraries to configure local normalization processes and make their own decisions on what data to keep or add.
Enabling the AI Metadata Assistant in Your Alma Environment
To enable AI Metadata Assistant, you must have the following roles:
- General Administrator
- Catalog Administrator
- Repository Administrator
The AI Metadata Assistant is disabled by default in all institutions.
Once administrators review this generative AI tool’s advantages and limitations, understand the risks and decide if and how their library works with it. They can accept the AI Metadata Assistant in Metadata Editor disclaimer under Configuration menu > Resources > Cataloging > AI Usage Profile by setting it to Yes and saving.
After the administrator enables the AI Metadata Assistant in an environment, catalogers with the AI Assisted Cataloging role can begin using it.
Testing In a Sandbox Environment
The AI Metadata Assistant settings are periodically updated using the Synchronize AI settings job. This ensures that the AI prompt remains effective and up-to-date as AI models evolve and change.
As scheduled jobs are disabled in Sandbox environments, before testing the AI Metadata Assistant, run the Synchronize AI settings to test with current settings.
- Select Monitor Jobs > Scheduled tab.
- Filter by Job Category = Data services.
- Select Run Now (available in Sandbox environments) from the Synchronize AI settings row actions.
After the job is completed, catalogers with the required roles can test the AI Assistant in the MD Editor. For more information, see Working with the AI Metadata Assistant.
Configuring the AI Metadata Assistant
To configure AI Metadata Assistant, you must have the following roles:
- General Administrator
- Catalog Administrator
Correcting Generated Metadata using a Normalization Process
To give libraries more control over the use of AI generate metadata, the institution can correct it using a normalization process. Normalization rules can be used to remove, replace or add metadata fields and subfields - for example, an institution can choose to add local fields relevant to its catalog, add a Data provenance subfield (e.g. $$7 in note fields) to specific fields if generated by the AI, remove certain fields that they don't want to contain generated metadata if generated, etc.
The selected normalization process is applied to the generated metadata in both the creation and enrichment workflows, before the resulting draft is available to the cataloger.
If the generated data is merged with an existing record (when enhancing a record with AI Assistant) or expanded from a template to add missing fields (when creating a new record), the normalization process is applied to the AI generated data only, before this merging takes place.
You can configure the normalization process that is used when working with the AI Metadata Assistant on the AI Usage Profile page (Configuration menu > Resources > Cataloging > AI Usage Profile), in the AI Metadata Assistant - other settings section.

Selecting a Merge Method for Enhancing Records with AI Assistant
When enhancing a record with AI Metadata Assistant, the generated metadata is merged with the enhanced record, the library's existing record is considered the preferred record.
Out of the box, the library's data is not overridden. The metadata generated by the AI is added to the record if:
- The field is repeatable
- The field is non-repeatable, and does not already exist in the preferred record
Institutions can control the use of data generate by the AI Metadata Assistant in the enrichment process by overriding the default merge rule and selecting a local merge rule, for example, select not to add certain repeatable fields (e.g. production and publication information) if already exist in the record, or override certain fields that are known to be problematic. For more information, see Working with Merge Rules.
You can configure the overriding merge method to be used when enhancing a record with the AI Metadata Assistant in the AI Usage Profile page (Configuration menu > Resources > Cataloging > AI Usage Profile).

Configuring the Metadata Request Types Sent to the AI Metadata Assistant
In addition to correcting the metadata suggested by AI using a normalization process, administrators can also select which types of metadata the AI is prompted to generate in the AI Usage Profile page (Configuration menu > Resources > Cataloging > AI Usage Profile), in the AI Metadata Assistant - other settings section.

Large Language Model generative AI tools are agile, and their responses differ between uses and evolve over time. The metadata returned by the AI varies each time, and may contain more or less metadata than what was prompted. Specifically requesting a certain type of metadata increases the chances of it being generated by the AI, but does not guarantee it.
You can remove a specific type of metadata from the request sent to the AI by disabling it in the Requested Metadata Configuration table. Lines in this table can only be enabled or disabled (the order and default value settings have no impact on the AI Metadata Assistant's work).

If summary is enabled, you can also select which type of summary request is sent to the AI:
- Ask for summary copy if available and generated if not (default) — the AI is prompted to try and copy the publisher's description if available in the data or images provided, attributed to the publisher, or if unable to do so, to generate a description of the resource in its own words.
- Ask for summary copy if available — the AI is prompted to try and copy the publisher's description if available in the data or images provided, attributed to the publisher.
- Ask for generated summary — the AI is prompted to generate a description of the resource in its own words.

Working with the AI Metadata Assistant
To work with the AI Metadata Assistant in the Metadata Editor, you must have both the following roles:
- Cataloger
- AI Assisted Cataloging
Working with the AI Metadata Assistant requires a dedicated role, in order to give libraries control over which catalogers work with generative AI tools.
You can use the AI Metadata Assistant to create a new bibliographic record, or enrich an existing brief record. Once the assistant completes processing the record, the draft containing its suggested metadata is pushed to the Metadata Editor for you to review and accept, correct or dismiss it. A real-time notification indicates that the draft is ready for you to work on.
Creating a New Record
You can create new records in the Metadata Editor using the AI Assistant.
- In the Metadata Editor, under New, select Create with AI Assistant. The New Record from AI Assistant pop-up opens.
New Record from AI Assistant fields: Field Description Title Mandatory. Provide the title of the resource to be created. Author Optional. Provide information on the resource author or creator. ISBN Optional. Provide a book’s ISBN. Content note Optional. Provide information on the resource content. Summary note Optional. Provide a summary of the resource. Record Format Currently only MARC 21 is supported. Expand from TemplateThe template to use when expanding the generated metadata.When selected, after the AI generated metadata is processed and normalized, any fields from the template that are missing would be added to the resulting draft record, to make sure no fields required by the library are missed by the cataloger.Alma remembers your selected template for future uses of the AI Metadata Assistant, so you only need to change this setting if you change the type of resource you're cataloging and need to use a different template.AttachmentsOptional. Upload up to four files containing relevant information about the resource (such as, a book’s back cover, table of contents, resource description received from the publisher, etc.).Supported formats are:-
JPEG
-
PNG
-
GIF
-
PDF — When uploading a PDF file, the first four pages are extracted and processed by AI.
-
DOCX — When uploading a Word (docx) file, the first four pages of the file are extracted and processed by AI.
You can select a file from your device or use your device's camera to capture images of the resource. The images can be cropped to focus on the area containing relevant information to improve the quality of the returned response.New for November! If your device has multiple cameras, you can select which camera to use.Requested MetadataDefines the requested types of metadata for the AI to generate. When selected, the AI is only prompted to generate the specific metadata requested. The options depend on administrator configuration (see Configuring the metadata request types sent to the AI Metadata Assistant), and are:-
All — Request the AI to generate all available metadata enabled by your administrator.
-
Request Subjects — Request the AI to generate subject suggestions.
-
Request Summary — Request the AI to copy and/or generate a summary note for the resource.
-
Request Content Information — Request the AI to generate a content note (relevant when providing the AI information on the resource's content, for example, an image of the table of contents or the song list of a CD.
-
Request Additional Metadata — Request the AI to generate any other available metadata that is enabled by your admin.
-
Alma remembers your selection for future uses of Create with AI Assistant, so you only need to change this setting if you change the type of resource you're cataloging and need to request different metadata.
-
Large Language Model generative AI tools are agile, and their responses differ between uses and evolve over time. The metadata returned by the AI varies each time, and may contain more or less metadata than what was prompted. Specifically requesting a certain type of metadata increases the chances of it being generated by the AI, but does not guarantee it.
-
- Select Generate Record to submit the information to the AI.
 Creating a new record with AI Assistant
Creating a new record with AI Assistant
You can continue working in Alma while the AI processes the information, and you are notified when the generated metadata suggestions are ready for you to work on in the Metadata Editor. For more information, see Reviewing AI Metadata Suggestions.
Enriching a Brief Record
You can enrich brief records.
- In the Metadata Editor, open the record that you want to enrich in edit mode. Under Editing Actions, select Enhance with AI Assistant.
The Enrich Record from AI Assistant pop-up opens, showing the title of the record you selected to enrich, so you can be sure you’re enriching the chosen record.
You can also attach up to four images of the resource, containing relevant information (such as a book’s back cover, table of contents, resource description received from the publisher, etc.). Supported formats are: JPEG, PNG, GIF and PDF (when uploading a PDF file, the first four pages of the pdf are extracted and processed by the AI).
You can select a file from your device or use your device camera to capture images of the Resource. The images can be cropped to focus on the area containing relevant information, to improve the quality of the returned response.
New for November! If your device has multiple cameras, you can select which camera to use.
-
(Optional) Select Requested Metadata if needed.
The Requested Metadata field indicates which types of metadata to request the AI to generate. When selected, the AI is only prompted to generate the specific metadata requested. The options depend on administrator configuration (see Configuring the metadata request types sent to the AI Metadata Assistant), and are:- All — Request the AI to generate all available metadata enabled by your administrator.
- Request Subjects — Request the AI to generate subject suggestions.
- Request Summary — Request the AI to copy and/or generate a summary note for the resource.
- Request Content Information — Request the AI to generate a content note (relevant when providing the AI information on the resource's content, for example, an image of the table of contents or the song list of a CD.
- Request Additional Metadata — Request the AI to generate any other available metadata that is enabled by your administrator.
- Alma remembers your selection for future uses of Create with AI Assistant, so you only need to change this setting if you change the type of resource you're cataloging and need to request different metadata.
- Large Language Model generative AI tools are agile, and their responses differ between uses and evolve over time. The metadata returned by the AI varies each time, and may contain more or less metadata than what was prompted. Specifically requesting a certain type of metadata increases the chances of it being generated by the AI, but does not guarantee it.
-
Select Enrich Record to submit the information to the AI.
-
The record is locked for editing until the AI processing is completed, and is available in MDE as a view-only record. You can continue working in Alma while the AI processes the information, and you are notified when the suggested metadata is ready for you to work on in the Metadata Editor. For more information, see Reviewing AI Metadata Suggestions.

Reviewing AI Generated Metadata Suggestions
When the draft containing the AI generated metadata suggestions is ready for you to work on, a notification containing a link to the draft in the Metadata Editor is displayed:

You can also see information on the completed AI Metadata Assistant tasks you've triggered in the Real-Time Notifications menu, in the Cataloging category:

In the Metadata Editor, draft records to be reviewed are marked with an "AI Generated" or "AI Enriched" badge, for easy identification, once the draft is reviewed and saved by the cataloger, this badge is removed:

The draft can be edited, saved, or dismissed as needed.
The unsaved metadata suggestions generated by the AI appear in purple to help catalogers identify and review them, or in orange if there are warning to be reviewed (fields with warnings appear that same regardless of source: an existing record, a template, or AI generated).


Working with the AI Metadata Assistant in the Alma Mobile 2 Application
The Alma Mobile app enables librarians to use a mobile device camera to process library resources. For example, perform a scan-in of an item barcode.
Catalogers with the AI Assisted Cataloging role can use it to easily take pictures of library resources and send them to the AI Metadata Assistant for processing.
Once the assistant completes processing the images, the draft containing the AI assistant’s suggested metadata is pushed to the Metadata Editor for the cataloger to review and accept, correct or dismiss it.
You can enrich an existing record by scanning the item barcode to retrieve the record to be enriched. Then, use your mobile device’s camera to take pictures of the item and submit them to the AI Metadata Assistant.
You can also create a new record by submitting a title and images (and filling in more optional information if you want).
For more details on the Alma Mobile app, see Introduction to the Alma Mobile 2 Application.
Submitting Feedback
To submit feedback on the quality of the generated metadata suggestions, click the AI feedback button in the MD Editor, while working on a draft which was created / enriched with the AI Metadata Assistant. This feedback is used to monitor and maintain the quality of AI-generated metadata over time.

Select the score you’d like to give the AI-generated metadata suggestions, from 1-5, and enter a comment to provide more details:

Identifying Records with AI Suggested Metadata
When a record is created or enriched using the AI Metadata Assistant, this information is maintained in Alma in two ways:
- MARC 21 metadata in the generated draft:
- A 588 Source of Description Note is added to the draft in addition to the AI-generated metadata suggestions. This field is searchable in Alma.
- If the AI generated metadata includes a 520 Summary Note, a Data provenance ($$7) subfield is added, indicating it was generated by AI (this is always added, whether the summary was copied from an image or created by the AI, since the AI process of copying data may introduce some changes to it).
- An administrator can also configure a normalization process that adds other fields or subfields to the draft (e.g. a local field containing information on the catalog's AI Metadata policies) - for more information, see Configuring the AI Metadata Assistant.
- Bibliographic record information: When a draft containing AI generated metadata suggestions is saved (without being released or discarded) - the information on the use of the AI Metadata Assistant is recorded and can then be viewed in Analytics and record versions.
Viewing AI Metadata Assistant Information in Analytics
AI Metadata Assistant information is available in the Bibliographic Details shared dimension of Analytics.
The Bibliographic Details for each record holds information on whether it was Created with AI or Enriched with AI.
This enables libraries to create reports on the number of titles created with the AI Assistant or enhanced with the AI Assistant.
For more information, see: Bibliographic Details.
Viewing AI Metadata Assistant Information in Record Drafts
For any records created or enriched using the AI Metadata Assistant following its official Go Live in February 2025, and consequently updated by another cataloger or process (generating a record version), it is possible to identify which version was created with the AI Metadata Assistant when viewing record versions:
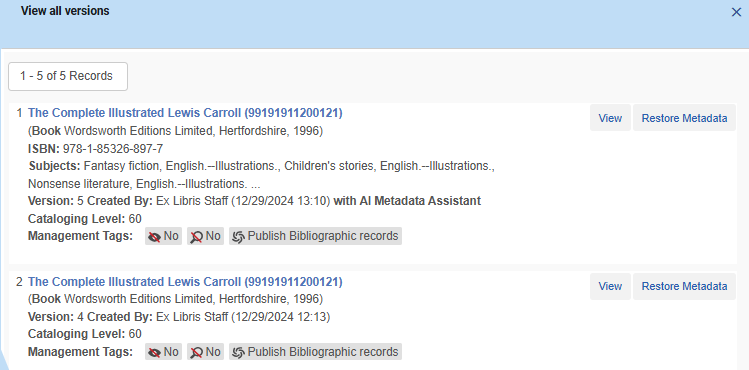
AI Icon Displayed in Title Search
In Alma's new title search UX, records created or enriched using the AI Metadata Assistant are displayed the AI stars icon, making them easy to identify.
Hovering over the icon shows a tooltip detailing whether the record was created with AI, enriched with AI, or both.

Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: Is the data I use to create or enrich the record used to train the AI?
A: No – we share the data with the AI for processing only, not to train it. -
Q: Where is the metadata coming from?
A: The metadata is generated by an AI LLM, according to the information provided by the cataloger (either manually or from a bib record being enriched). Currently, the input information supported is bibliographic metadata such as the resource’s title (which is mandatory), as well as files containing images of the resource (e.g. title page, back cover, table of contents, publisher description).As with all AI models, the model’s training data is also used to generate a response – this includes knowledge of MARC fields and subfields, relevant LC subjects, and if information on the specific resource exists in the AI model’s training data (e.g. publishing year, author’s birth year, resource description) – that may be used in the generation of the metadata as well.
-
Q: Does the AI perform an online search to get data for me?
A: No – our AI platform is not using online searching, the metadata is generated based on the information provided by the library, and that which exists in the AI training data. -
Q: If I upload images of books – are they saved anywhere?
A: No, we only use the image to suggest metadata, we don’t save it for any other use. -
Q: Will the AI catalog for me?
A: The AI assistant suggests metadata for review by a cataloger.
The cataloger reviews it and can accept, correct or reject the suggestions. Since Generative AI may result in inaccuracies or biases in the output - combining the human and technological abilities allows for a more streamlined, efficient cataloging experience, while maintaining data integrity. -
Q: Why am I getting different metadata suggested for the same resource each time I use the AI Metadata Assistant?
A: Large Language Model generative AI tools are agile, and their responses differ between uses and evolve over time. The metadata returned by the AI will vary each time according to the information provided to it, the resource being cataloged, and the AI’s internal processing itself. -
Q: Can the AI Metadata Assistant be used to enrich any record in the catalog?
A: No – the AI assistant can only be used to enrich records that aren’t locked for editing, and that I’m allowed to edit according to my cataloging role and level.
In addition, Phase I supports only records in MARC 21 format, and does not support enriching CZ records.
For network members – the ability to create or enrich network records also depends on the network’s settings. -
Q: Phase I supports English MARC 21 cataloging of books, using LC authorities – what’s planned for the next phases?
A: We’re talking to libraries around the world to understand workflows and assess needs, to decide with the community what to focus on next. Options include more workflows, more cataloging languages and more subject vocabularies. -
Q: How are you making sure the returned subjects are real?
A: We check that the returned subject matches an existing authority record, and will link to it either fully or partially. It may match either the preferred or non-preferred term - if a non-preferred term is suggested by the AI, it can be updated to the preferred term either by the cataloger, using F3 in the Metadata Editor, or automatically by the scheduled "Authorities - Preferred Term Correction" job (for more information see Jobs Related to Authority Records). -
Q: Can the AI provide any MARC 21 field?
A: No. We ask the AI assistant to generate the most useful fields, maintaining a balance of helpfulness and accuracy, and Alma is processing the suggested metadata fields from the AI and presents the suggestion to the cataloger in record draft format, for easy review and workflow. We are working with the community to assess and decide on the usefulness of the different fields.
The AI may also generate unrequested fields, which may contain helpful information. Since the AI generates metadata in a probabilistic way, it may sometimes also generate irrelevant fields such as local fields, system numbers, or record provenance which doesn't represent a record (as no record is being copied, only specific metadata is being generated) - such fields likely contain irrelevant or generic data, and when processing the results, Alma removes these. -
Q: Will everyone in the library be able to use the AI Metadata Assistant?
A: The library controls the access to this: The AI Metadata Assistant workflow is embedded in the Metadata Editor - I need to be a cataloger to be able to create or edit bibliographic records, and also have the new AI Assisted Cataloging role to use the new workflows. -
Q: Can I choose not to use AI enriched data in my library?
A: Of course! The library has full control of using this tool. To work with the AI Metadata Assistant, the library’s general administrator should first enable this for the institution in the new AI Usage Profile configuration page. -
Q: I am a network member – can AI be used to enrich network records?
A: Of course! If the network enables the AI Metadata Assistant, any members who also enable it in their institution will be able to use it to enhance network records. -
Q: My network restricts some fields from editing – will the AI be able to create them anyway?
A: No. Any restrictions enforced by the network also apply to the AI Metadata Assistant workflow – catalogers will only be able to use it to create or enrich metadata they are allowed to create or enrich manually. -
Q: What LLM are you working with?
A: Models are subject to change as models and capabilities evolve. As of the February 2025 release, the AI Metadata Assistant was working with the gpt_4o_2024_08_06 LLM model.

