General
General
Does Alma support the management of digital resources?
-
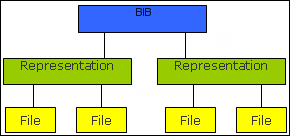
Bibliographic record – The top level consists of the bibliographic record which contains the metadata of the resource. (This is also true for physical and electronic resources.)
-
Representation – Under the bibliographic record level is the representation level. This level acts as a container for the digital files. Multiple representations can be attached to the bibliographic record. One representation can be the master copy and another a derivative copy and can differ in format, resolution, or size.
-
File – The third level is the file level—that is, the digital files of the resource. There can be several files in each representation.
-
Remotely - Alma allows you to store your digital files remotely in a digital management system system while maintaining the bibliographic records in Alma.
-
Non-Remotely - You maintain all of the digital resource information in Alma, such as bibliographic records, representations, and files.
Does Alma support the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH) for import and export of data?
What flows do Alma and Primo support in order to manage digital resources?
(Clarification: Digital resources refers to files which are owned by the library, as opposed to electronic resources.)
- Alma repository: Files are uploaded to Alma’s storage layer (Amazon S3) and fully managed by Alma as digital inventory, in addition to metadata management. Alma publishing can be enriched to include links to these resources. Read further here regarding services and flows provided by Alma for this model.
- Remote repository: Institutions can integrate their local Digital Asset Management System (such as Rosetta or DSpace) within Alma. The remote digital system provides bibliographic metadata records via the OAI-PMH protocol, which is then synced with Alma’s catalog. The digital files continue being maintained in the remote repository, while the metadata could be managed and published to discovery from Alma. Read further here regarding services and flows provided by Alma for this model.
- Bibliographic reference: URLs cataloged in bibliographic records, e.g. the MARC 856 field or Dublin Core dc:identifier field, pointing to files stored on the library’s local servers. These can be managed and published in Alma, similar to any bibliographic field. However Alma does not provide any digital-specific services for the resources.
- Primo harvesting: Digital repositories can publish records directly to Primo in order to expose content publicly. Published metadata can be normalized in Primo VE’s configuration in Alma. Read further here.
The first two models require an Alma Digital license, as described here.
Should we be concerned with data privacy?
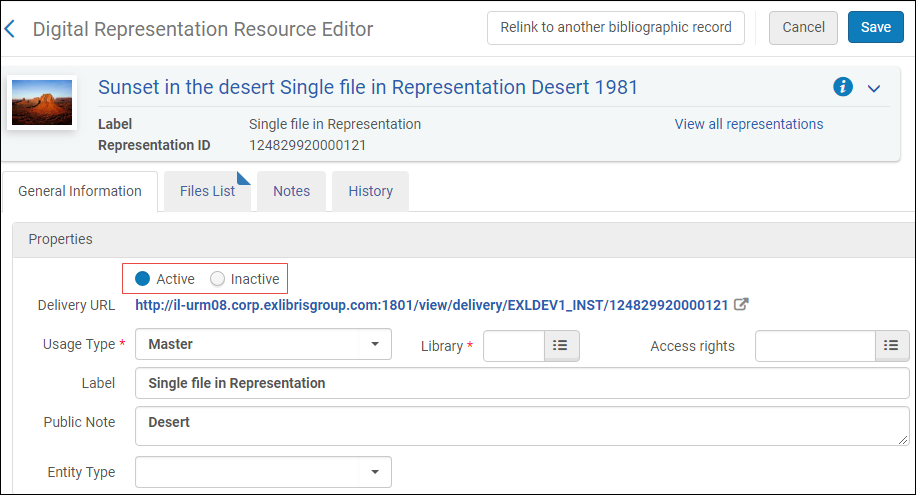
Can digital representations be hidden from patrons?
You can mark a digital representation as active or inactive. Inactive representations are hidden from patrons in their discovery systems.
The active/inactive button is available in the following:
- Digital Representation Resource Editor
- Staff Mediated Deposit page
- Add Digital Representation page
- Digital import profile – Inventory tab
Where can I find information about relevant external interfaces?
Storage
How is the storage of digital objects handled in Alma?
How will storing digital objects affect Alma’s response time?
Where are digital objects stored?
Is storing objects in Amazon a cost effective solution?
Viewers
Does Alma support the viewing of digital files?
Digital content which is published to external discovery systems holds a delivery URL which points to the digital objects. For objects stored locally in Alma, the Alma viewers can be used. The Alma viewer, which can be seen below, can render any format displayed natively by the browser. Other formats can be downloaded and opened by the patron in dedicated software:
In addition, Alma supports the International Image Interoperability Framework (IIIF) and enables viewing digital images in Alma using a built-in image server and the Universal Viewer. The Universal Viewer has the ability to display and zoom in on high-resolution images and supports formats such as tiff, jpeg, and jpeg2000. The advanced Internet Archive Book Reader has also been embedded into Alma, based on the IIIF framework and supporting full-text search:
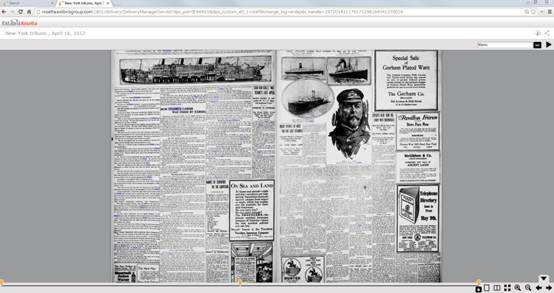
Alma supports also the use of third-party digital viewers, which enables customers to use their own viewers for viewing digital content managed in Alma.
Does Alma support streaming video and audio for the Alma Viewer?
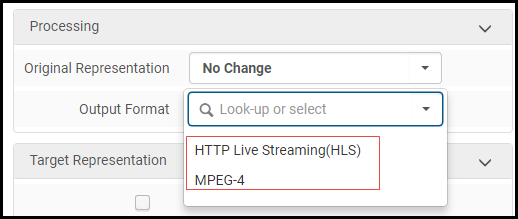
The Alma Viewer supports streaming video and audio. You can convert existing digital representations to streaming format using the Media Conversion Job. The job creates a new representation for the converted format that Alma can use to display streaming video and audio.
The job has two output formats, HTTP LiveStreaming (HLS) and MPEG-4.
Is there support for native IIIF viewers?
Alma supports the International Image Interoperability Framework (IIIF) and enables viewing digital images in Alma using a built-in image server and the Universal Viewer. The Universal Viewer has the ability to display and zoom in on high-resolution images and supports formats such as tiff, jpeg, and jpeg2000.
Does Alma support third-party digital viewers?
Alma supports the use of third-party digital viewers, which enables customers to use their own viewers for viewing digital content managed in Alma. For more information, see the Developer's Network.
Total views:
2790
