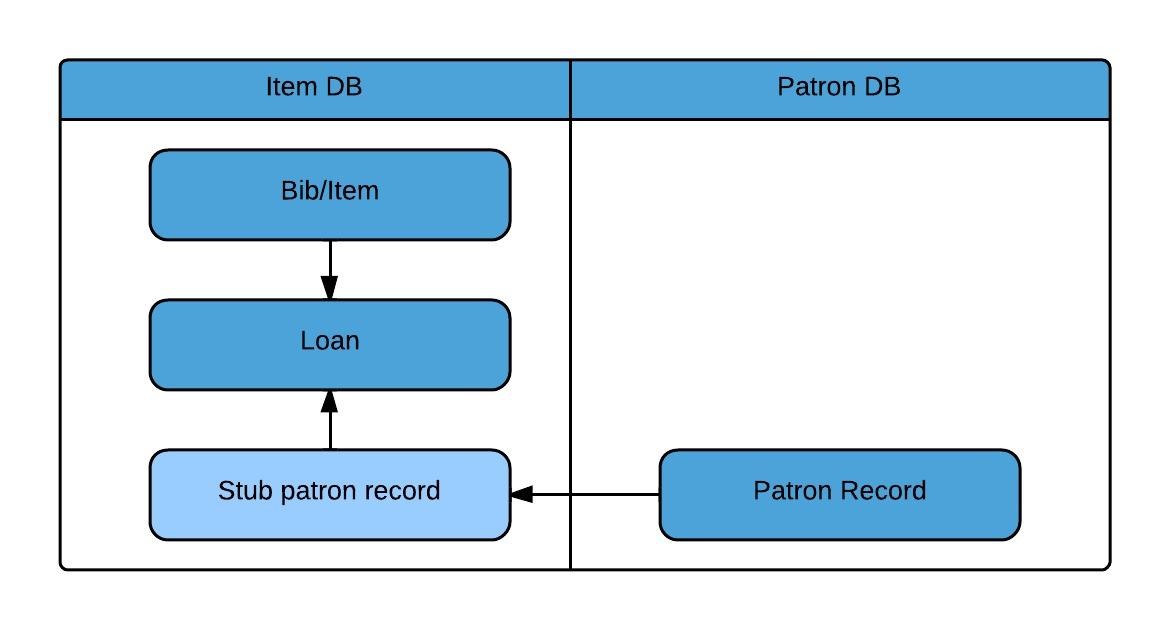
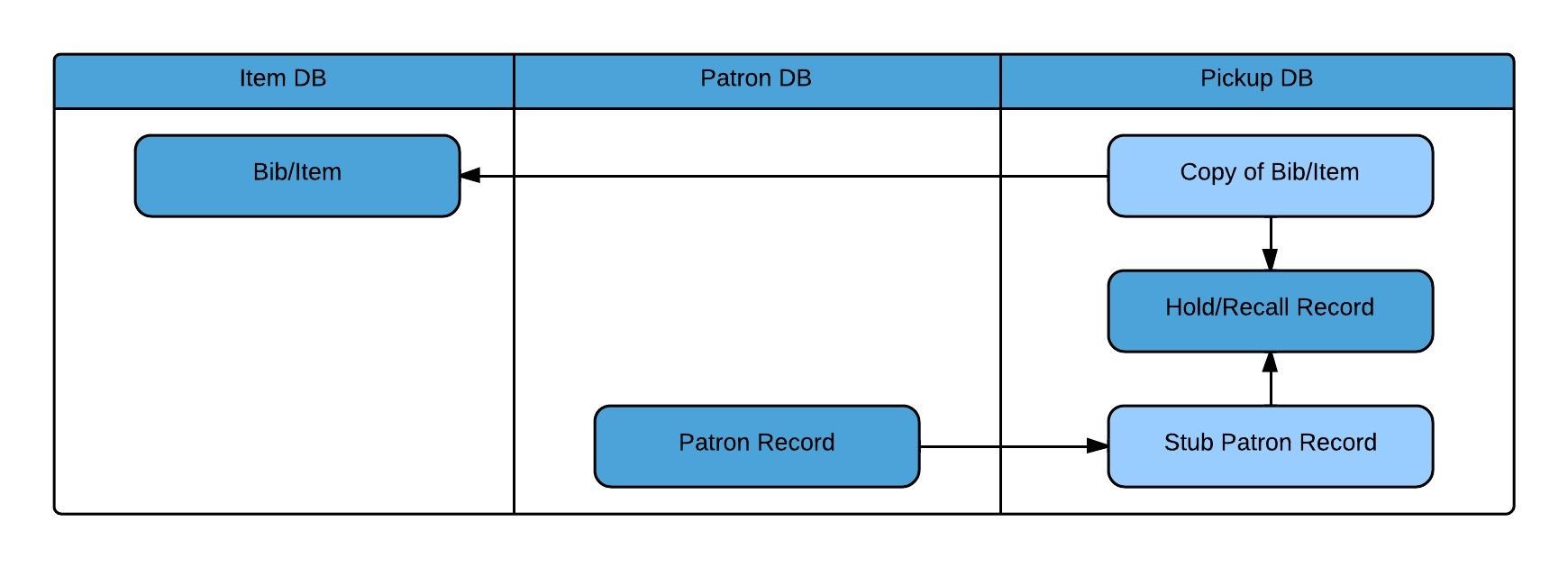
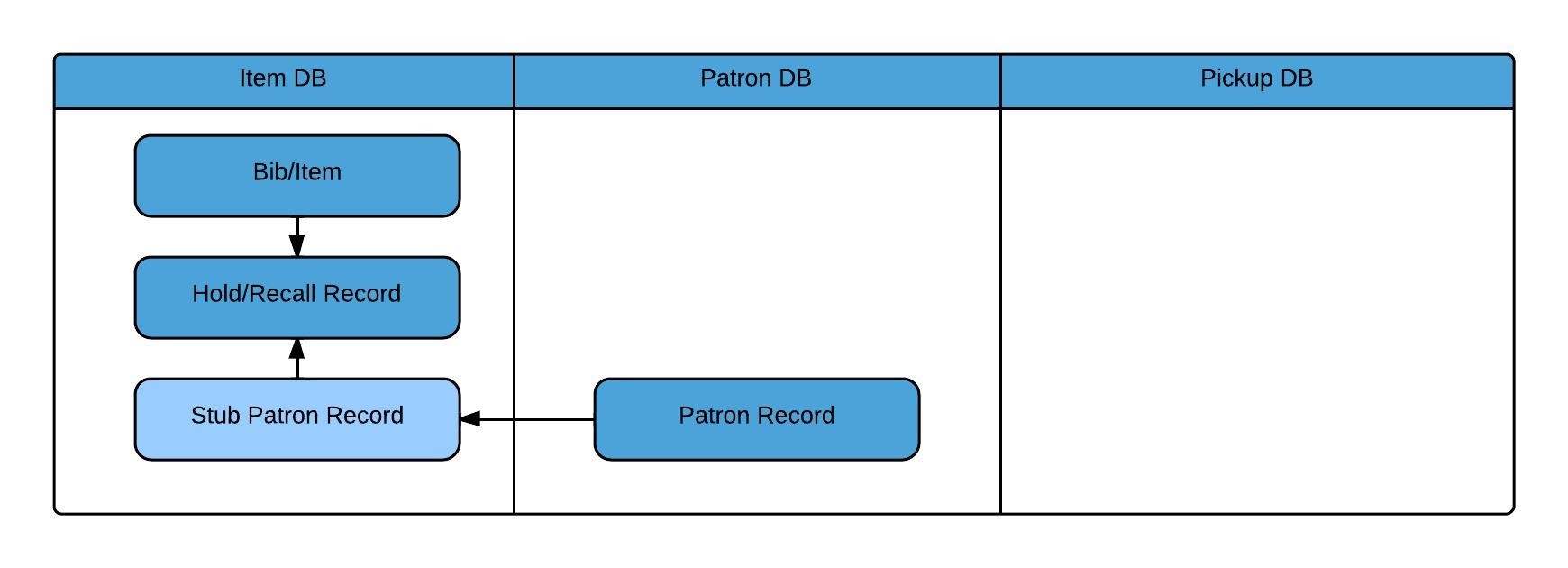
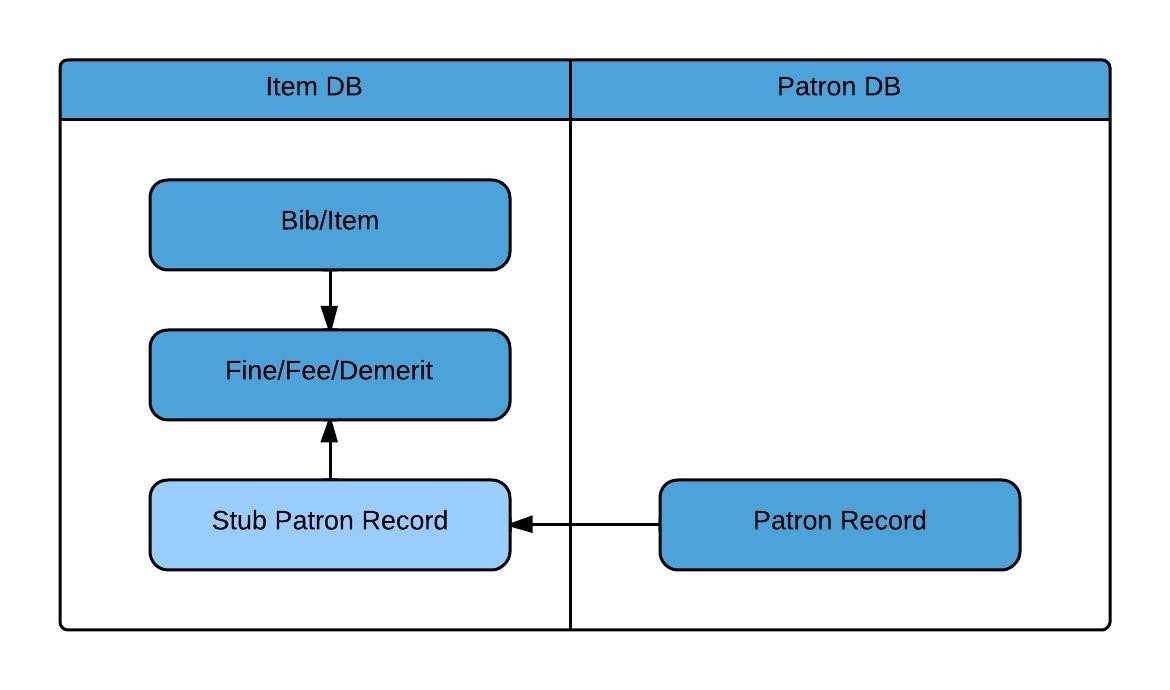
Inventory consists of holdings and item records from your source ILS as well as electronic resources from your electronic link and resource management systems, such as SFX and Verde.
Print inventory is managed at the institutional level. Initially, all records (bibliographic, holdings, items, patrons, orders, etc.) are loaded into the individual IZ.
The methods used for the New Shared Catalog and the Previous Shared Catalog types are explained in different sections, since they are not exactly the same.
New Shared Catalog
This section describes the print inventory process for sites which previously had separate cataloging environments.
The contribution process for a new shared catalog used in migration is similar to the regular ongoing Alma contribution process, however it has many fewer options. The primary goal of the migration NZ contribution process is to build the NZ catalog quickly and efficiently outside of Alma using file processing, based on matched identifiers. This section describes the migration process.
The migration programs build a deduplicated bibliographic file using the individual bib files from each institution. All records from the files are included, even if any record does not have the specified prefix. The institutional bib files are processed in the order that is specified by the customer. The process order is important since the first record into the NZ is used as the Master record.
- If an identifier exists and a matched record is not found in the NZ, the IZ record is contributed to the NZ and becomes the master NZ record.
- If a match is found in the NZ, the IZ record is not contributed. Linking is done later.
- See the section below about Local Extensions for information on how subsequent institutions may retain local information in locally defined tags.
Special situation about matching records in the same bulk: When the new shared catalog is created, records are contributed in bulks of 100. If two or more records are equivalent and in the same bulk, AND the records are new (there is no existing match for this in the NZ), then all records are contributed to the NZ.
The deduplicated bib file is then loaded to the NZ. At the same time, the individual institutions are processed using the normal migraion process and loaded to their IZ.
After the NZ and IZ are loaded, a process is run to link the IZ records to the NZ records. The IZ maintains the Alma bibliographic record identifier (MMS ID) of the original IZ record in order to provide a base to which all other administrative data linkages (holdings, items, orders, loans) can attach.
Once a bibliographic record from the IZ is linked to an NZ master catalog record, changes to the master are automatically reflected in all linked bibliographic records and all members linking to it. Localization of each linked IZ record is optionally supported via a defined set of supported local extension fields.
Post production, the Alma contribution method is used. More information on working with a Network Zone in Alma can be found in the guide
Network-Managed Records in a Network Zone.
Local Extensions (MARC)
Consortia members who share bibliographic records may still want to maintain some local information in their IZ record. This can be accomplished through the use of local tags.
Tags in the MARC 09x, 59x, 69x, 77x/78x, and 950-999 ranges that are marked with subfield 9 LOCAL (upper case) are saved in the IZ as local extensions to the master bibliographic record. Tags that are not in these ranges, as well as tags in these ranges that are not marked with subfield 9 LOCAL are not saved in the IZ. Sites can identify any tags in 09x, 59x, 69x, 77x/78x, and 950-999 ranges that they want to keep locally, make sure they are in the specified ranges, and then mark them with a subfield 9 with only the word LOCAL (no spaces, punctuation, or any other characters) when providing the institutional IZ level records.
If you have 880 fields which are connected by $6 to a local tag, do not include $9 LOCAL on the 880. The migration program will detect that the 880 is linked via the $6 and treat the related 880 as a local tag.
If the above specified fields do NOT include a subfield 9 LOCAL ($9 LOCAL, where LOCAL is in all upper case) in the field, then the fields are subject to the NZ first-in routine. If the record is the first to be contributed to the NZ, then the tags will be saved to the NZ part of the master NZ record. If the record is not the first record contributed to the NZ, then no tags in this record are saved locally and the master (first-in) record is what is used in the NZ for this consortium.
Customers may either add the $9 LOCAL to their records prior to submitting to Ex Libris, manually or by using tools in the previous ILS, or they may use the NZ_LOCAL_TAGS question on the Migration Form, questionnarie tab. Do not use both! If you add $9 LOCAL and then also specify tags, you will end up with double $9 LOCAL.
For local fields in NZ or IZ: if local fields are used, Ex Libris recommends that the NZ use fields 900-949 and the IZ uses 950-999. This way the local NZ fields (900-949) are those that are local to the entire consortium where every institutional member uses them, and the local IZ fields (950-999) are those that are local only to the single institution. This is recommended because it is important to be able to retrieve groups of records based on data in specific local fields, and having the same local field used for two different data elements may cause problems in retrieval. During migration, if a 900-949 tag has $9 LOCAL subfield, it is removed and the tag is kept in the NZ.
Local Extensions (Unimarc)
For bibliographic records using Unimarc, the local extensions operate the same way as MARC local extensions, except that the ranges are defined as XX9, X9X, and 950-999.
Contents of the NZ Record
During the migration process, the contents of the NZ record are the contents of the first record of the group. When a record is added to the NZ and no match is found, the record (without local extensions) is added to the NZ and the local extensions are added to the linked IZ record.
When a subsequent record is matched to the NZ record, the subsequent record’s local extensions are saved to the linked IZ record, and all other tags from the subsequent record are discarded in favor of the first-in NZ record.
Matching
Generally, the NZ linking programs use values in the MARC/UNIMARC/KORMARC 035 $a and 035 $z fields to determine a match. Further information on options for that match is listed in the following sections.
Extraneous Identifiers
Customers must ensure that there are no extraneous identifiers in their bib records which may interfere with proper matching. If using non-OCLC matching, Ex Libris recommends to use a unique prefix for the unique identifier which cannot be confused with other identifiers. If using OCLC matching, there may be extraneous OCLC numbers in the bibliographic record for one reason or other.
In particular, the migration programs automatically copy the contents of the 001 (identifier) and the 003 (prefix) into an 035 during migration. Some former systems such as Symphony and Millennium/Sierra keep an OCLC number in the 001; during migration this copied to the 035.
Sometimes the 001's OCLC number is good, but sometimes it is bad/incorrect.
Since this number may interfere with matching, Ex Libris recommends to remove these numbers from the 001 prior to migration if there is any chance its movement to 035 may interfere with NZ matching.
Regular (Non-OCoLC) match method
Customers should specify a prefix to be used for the NZ contribution process. The NZ matching process will only look at numbers with the specified prefix.
For example a single bib record may have data in three different 035 $a fields:
035 $a (abc)1234567
035 $a (def)1243456
035 $a 3345671
If the customer specifies '(abc)' as the prefix, only the number 1234567 from the above list will be used to detect matches, and then only with other numbers with the (abc) prefix.
Do NOT rely on the Alma migration process which moves an 001 system number and 003 prefix to an 035, as described in local migration guides. Depending on NZ setup, this number cannot be counted on to be placed/moved prior to NZ contribution and/or linking. Customers should provide the numbers with prefix in the 035 $a of the delivered file.
Partial matching
It is possible to request to use partial string matching. For example, it is possible to request that the prefix be "*_Z", so that the following two numbers match.
AB_Z(12345)
CD_Z(12345)
The partial string matching may also be at the end of the number, for example using "01cust*" may be used to specify a match between the following two numbers:
12345-01cust_abc
01234-01cust_def
The above matching cannot be used in combination with the OCoLC matching as described in the next section. You can either use a specified prefix, or you can use OCLC matching, but you cannot use both.
Customers who wish to not use the 035 $z (cancelled control number) may make a special request of the Ex Libris migration team. The two options for matching are:
- 035 $a and 035 $z
- 035 $a only (by special request)
OCoLC match method
The OCLC numbers are often inconsistent.
If an OCLC number has the prefix (OCoLC), remove the prefix ocn, ocm, or on from the number portion of the OCLC number, and use only the value in parentheses to compare. This means that the following are considered equivalent:
- (OCoLC)12341234 is the same as (OCoLC)ocm12341234
- (OCoLC)567856789 is the same as (OCoLC)ocn567856789
- (OCoLC)23456789 is the same as (OCoLC)on23456789
This is accomplished by a normalization routine as described below.
The normalization routine does not permanently modify the OCLC numbers; the 'modification' is only performed at the time of match, and the identifiers are kept as is.
The OCLC match method always uses both 035 $a and 035 $z for matching. It is not possible to limit to 035 $a using this match method.
Normalization Flow for OCLC match method
035a and 035z = 'OCLC Identifier' Normalization Flow:
for each
MARC "035"|"a" AND MARC "035"|"z" value as '(Prefix)'||'ID'
normalize lower_case '(Prefix)'||'ID'
normalize OCLC prefix ('Prefix') for (ocolc)' OR '(oclc)' AS '(ocolc)'
remove initial zero padding ('ID')
remove OCLC padding ('ID') for 'ocm' OR 'ocn' OR 'on'
end
For example:
- 035 |a (OCoLC)41319586 is normalized to: (ocolc)41319586
- 035 |z (OCoLC)ocn41319586 is normalized to: (ocolc)41319586
- 035 |a (OCoLC)ocm00041319586 is normalized to: (ocolc)41319586
- 035 |a ocm00041319586 is normalized to: (ocolc)41319586
If a number has an (OCoLC) prefix and another prefix too, like (OCoLC)abc12345, then the number abc12345 is included in the OCLC match process, and will match other numbers like (OCoLC)abc12345.
Multiple Matches
Matches and linking are only executed when there is a single match in the NZ. If there are multiple bibliographic records found in the NZ that match the record attempting to link based on the identifier, the record is not considered a match. The case here is if a single 035 in a single incoming IZ record matches multiple records in the NZ. This usually happens when one or more bib records have multiple OCLC numbers in the record, either already in the NZ or in the incoming IZ record.
The results of this multiple matching is that the record IZ is reported as a multi-match and is not linked to the NZ. Using Alma tools, this type of outlier duplication in NZ central catalog generation can be rectified and re-linked in smaller batch sets post-migration.
Multiple Incoming Identifiers
If the incoming IZ record has multiple chosen identifiers, the linking program looks for matches from all identifiers. If only one match is found in the NZ from all of the possible identifiers, the record is a match. However, if multiple identifiers from the incoming records each find a match in the NZ, the record is not considered a match. See Multiple Matches, above.
Multiple Matches Within the Same Institution
There should not be multiple records with the same match identifier within the source file of a single institution. If multiple matches in a single IZ are provided, the first one found links to the record in the NZ, and the others do not get linked - they remain local records.
Consequently, you may consider combining these records in your source ILS prior to migration. Multiple bibliographic records for the same OCLC number may be a holdover from previous cataloging practices in an isolated ILS, but in Alma with a Network Zone topology, multiple IZ bib records linked to the same NZ master cannot be searched and retrieved.
Records not Contributed to the NZ (for New Central Catalogs)
Some records do not contain the type of ID key relevant for contribution to the NZ during migration of new central catalogs. These records are usually:
- Migration-generated boundwiths (where the linkages are built based on IZ specific inventory)
- Other local institutional records that have no relevant ID
Suppressed Records
When building the NZ, it is typically recommended that all shared catalog records are not suppressed so that each IZ can decide on its own to suppress behavior. That is, each IZ linked to a central catalog record can decide to suppress it for its own purposes. Suppression in Alma can also be done at the holdings administrative level as well, when needed. In this case, when records are exported to Primo, the bibliographic record is exported, but no services (holdings) are listed as being available. Only when a shared catalog record is definitely to be suppressed for all members equally should Bib-level suppression be used in the central catalog.
During the building of the NZ, the first record into the NZ determines the suppression of the entire NZ record. Records from the IZ will link to the NZ with no regard for suppression, and the subsequent records matched will automatically have the suppression level of the first in NZ record.
In some cases, depending on file input and/or timeline, the NZ is built with all records being unsuppressed. If it is possible to process the NZ early, then this is the preferred method, but it is not always the case. Be sure to check with your project team to know if suppressed records are considered when building the NZ.
The functionality of an NZ suppressed record in Primo is determined by other factors. See the powerpoint:
The suppression of records in the Network Zone and Member Institution and how it Influences Primo Discovery.pptx for more information.
Ignore CZ records
By default the parameter
ignore_cz_records is set to false. If you do not want to include CZ-linked records in the linking process, inform your migration analyst so they can change it to true. This should be set on the Network level.
Links Between Records
There are three methods for providing links between two records in a consortial environment in Alma.
- Relationships are built based on the standard MARC/UNIMARC/KORMARC linking fields between bibliographic records. One direction of linking is sufficient to create the bi-directional linkage, meaning that only one of the bibliographic records needs a tag.
In order to see More Info related records in Alma, the bibliographic record and its target linked bibliographic record must exist in the active institution in which you are working in Alma. That is, if both bibliographic records linked together are in the NZ, a "More Info" link is displayed. If only one of the two bibliographic records is in the institution in which you are working, the More Info link is not displayed in Alma.
- Alma's end-user services menu (GetIt and ViewIt) do bring in relationships across the consortium, however. That is, if the Alma resolver does not find a related record match in the Institution Zone, it searches for matches in the NZ as well. If it finds a match in the NZ and that match has related records, the Alma resolver searches the IZ for the record that links to the related record found in the NZ.
The services menu approach is intended to be used via Primo only where all services are offered.
- It is possible to enrich the standard Bib-level link with an additional pointer on the Bib linkage to the level of an item in the target record by putting issue information into the $g subfield with the following prefixes:
- No – provide the specific chronology A OR barcode of the linked item
- yr – provide the YYYY year of the linked issue
- iss – provide the issue # of the linked issue
- p – provide the specific page of the linked issue
Previously Shared Catalog
This section describes the print inventory process for sites loading the NZ first, where the sites previously had a single shared cataloging environment. This method is typically used when the number of shared bibliographic records is large and there is a time savings by pre-loading bibliographic records into the NZ.
When using the Previously Shared Catalog method, each record must be delivered at least twice: once in the large consortia file destined for the NZ, and once in the local IZ file along with the administrative data for the local record (items, orders, etc). There must be a link between the records using a unique key, usually an identifier from the system that managed the previously shared catalog, but any unique key may be used.
If the different IZs are coming from different library systems, and a central office wishes to provide a similar master bib file, it is possible to use another shared bibliographic identifier as the unique match key. For example, the shared unique bibliographic identifier may be the number from a national bibliographic agency such as OCLC, SUDOC, or SBN. In this case, the master bib file contains a set of bib records with the unique bibliographic identifier, and each IZ contributes a set of bibliographic records where each bib contains both the unique bibliographic identifier (used for matching to the master file) AND ALSO the local bibliographic number of the local system (used for matching to the local item, order, and other administrative data).
The migration team loads the entire shared deduplicated set of bibliographic records to the NZ before any other IZs are migrated. The bibliographic records in the IZ are matched against the NZ bibliographic records, using the single shared bibliographic identifier of the previous system or other unique key.
- If a match is found in the NZ, the migration programs create a local IZ record with just the local extensions and load that to the NZ.
- If no match is found in the NZ, the migration programs load the entire record to the local IZ. This is unlikely but possible depending on the functionality of the previous system.
There should not be any multiple matches in this case, since there is only one identifier and it should be unique per master record.
Local extensions are defined here the same way they are defined in the New Shared Catalog section above.
Extraneous Identifiers
As with the New Shared Catalog, customers must ensure that there are no extraneous identifiers in their bib records which may interfere with proper matching. It is recommended to use a unique prefix for the unique identifier which cannot be confused with other identifiers. In particular, if a number from a national bibliographic agency such as OCLC is used, there may be extraneous numbers for one reason or another, using the same prefix.
In particular, the migration programs automatically copy the contents of the 001 (identifier) and the 003 (prefix) into an 035 during migration. Some former systems such as Symphony and Millennium/Sierra keep the OCLC number in the 001; during migration this copied to the 035.
Sometimes these numbers are good, and sometimes these numbers are bad/incorrect.
Since this number may interfere with matching, Ex Libris recommends to remove these numbers from the 001 prior to migration if there is any chance its movement to 035 may interfere with NZ matching.
Links Between Records
With the Previous Shared Catalog method of creating the NZ by loading the NZ first, links between records continue to work the same as described above in the New Shared Catalog section. However, keep in mind that when loading the NZ first, there is a possibility for bibliographic records without inventory to NOT be represented in a local IZ.
When using the New Shared Catalog method where the IZs are loaded first, if there is a bibliographic record without inventory in the local IZ, it gets merged to the NZ. The local IZ maintains the representation of that bibliographic record in the IZ.
When using the Previously Shared Catalog method where the NZ is loaded first, if there is a bibliographic record without inventory that was provided in the local IZ file, a representation of the bibliographic record will NOT be made in the local IZ if there is no inventory or no local extensions.
Therefore, if there are bibliographic records without inventory that need to link to other bibliographic records in the local IZ, the bibliographic records should either have inventory or have a local extension tag. This local extension might be very small and insignificant such as the institution code in a single subfield.