Configuring Metadata
Configuring Metadata
This section contains:
- Understanding Rosetta Metadata
- Configuring the DC Editor
- Configuring Intellectual Entity (IE) Types
- Configuring IE Status
- Configuring Subformats
- Configuring the OAI Server
Understanding Rosetta Metadata
Each content object (such as an intellectual entity (IE), a representation, or a file) in the Rosetta system is accompanied by information — known as metadata — that describes the semantic and technical characteristics of an object. The Rosetta system uses metadata to conduct a more efficient search of content objects, as well as to provide additional information about content to content consumers.
The Rosetta system supports metadata that originates both within the Rosetta system, and in external systems, as described in the following table:
| Metadata Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Local |
|
| External | Any metadata stored in an external system, such as a collection management system (CMS) Assessors and Arrangers can import external metadata to the Rosetta system by assigning a CMS ID to a content object. (For more information, see Assigning a CMS ID to an Intellectual Entity in Part IV, Assessors, Arrangers, and Approvers, of the Rosetta Staff User’s Guide.) |
Configuring the DC Editor
Staff users add descriptive information using the DC Editor.
Administrators can edit the DC Editor configuration file to define how the DC Editor must process both the elements and their contents. When editing the configuration file, Administrators can define the following parameters:
- DC elements that must be available to staff users
- Element qualifiers, including the type of the information that the qualifier holds (such as text, integer, or control list)
- The element type and the operators available when searching for the DC field. For example:
- DATE – Accepts a date value and uses operators such as Before and After.
- TEXT – (Default) Accepts a text value and uses operators such as Contains Keywords and Starts With.
- STRING – Accepts a string value and uses operators such as Equals and Does Not Equal.
- NUMBER – Accepts a number and uses operators Equals, Greater Than, and Less Than.
If you change the element type, a reindexing job must be run for the elements to be searchable under the new type.
- Validation routines that must be run on the document, element, and qualifier levels (such as checking whether a staff user completed all mandatory elements)
- Correction routines that must be run on the document, element, and qualifier levels (such as putting the current date into the mandatory Date element that a staff user left empty)
Administrators can access the DC Editor configuration file starting on the Advanced Configuration page and linking through the following pages: Repository > Metadata > DC Configuration.
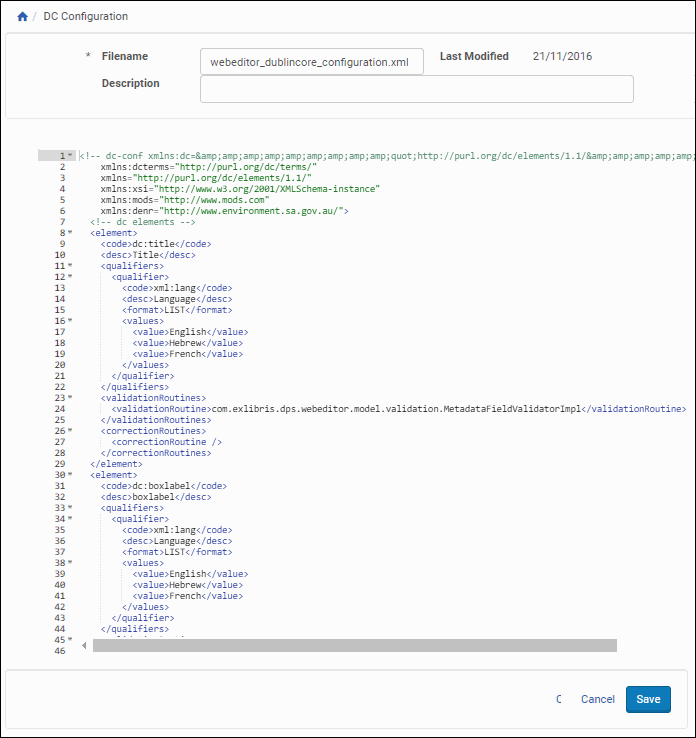
Dublin Core Configuration File
Administrators work with the DC editor configuration file as they do all configuration files. For more information, see Working with Configuration Files.
Configuring Intellectual Entity (IE) Types
When staff users configure the Rosetta system, they select one of the IE types from the list of predefined options. Administrators define these options during advanced configuration, using the IE Type code table. (For more information about accessing the IE Type code table, see Administration.)

IE Type Code Table
Administrators work with the IE Type code table as described in Working with Code Tables.
Configuring IE Status
When staff users configure the Rosetta system, they select one of the IE statuses from the list of predefined options. Administrators define these options during advanced configuration, using the IE Status code table. (For more information about accessing the IE Status code table, see Administration.)

IE Status Code Table
Administrators work with the IE Status code table as described in Working with Code Tables.
Configuring Subformats
When staff users configure the Rosetta system, they select one of the file subformats from the list of predefined options. Administrators define these options during advanced configuration, using the File Subformat code table.

File Subformat Code Table
Administrators work with the File Subformat code table as needed.
Configuring the OAI Server
oaiproviderconfig.xml contains configuration details for your OAI server, including values returned through the Identify protocol request and maximum number of objects returned per ListRecords and ListIdentifiers request.
Repository Information
Users can edit the oaiproviderconfig.xml configuration file to provide information about the repository as specified in http://www.openarchives.org/OAI/openarchivesprotocol.html#Identify, according to the following guidelines:
| Field | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| repositoryName | Rosetta | Can be replaced |
| baseURL | Should match your Rosetta delivery load balancer hostname and port | |
| protocolVersion | 2.0 | Should not be changed |
| earliestDatestamp | 2000-01-01T00:00:00Z | Can be edited to reflect a more recent date; format must conform to YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssZ granularity |
| deletedRecord | persistent | Rosetta currently does not support OAI set deletion, so this should not be changed |
| granularity | YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssZ | Should not be changed |
| adminEmail | Can be replaced | |
| ListRecordLimit | 1000 | Can be replaced; in case of large records timeouts may occur, in which case a lower limit should be applied |
| ListIdentifiersLimit | 2000 | Can be replaced; in case of timeouts a lower limit should be applied |
| scheme | oai | Should not be changed |
| repositoryIdentifier | Should match your Rosetta delivery load balancer hostname | |
| delimiter | : | Should not be changed |
| sampleIdentifier | Concatenation of {repositoryIdentifier}:IE1000, e.g. rosetta.myinstitution.org:IE1000 |
Metatadata Formats
metadataFormat elements should reflect the list of formats as configured in the OAI Metadata format code table. The metadataPrefix element should match the row’s code field value.

