Searching in the Esploro Research Hub
You can search Esploro using the persistent search box located at the top of every page. The persistent search box offers you a simple or advanced search.
Watch the Searching and Creating Sets video (5:50).
For information on searching in the portal, see Searching in the Esploro Portal.
You can search for the following Esploro entities (search types):
| Search Type | Notes | Results Page | Fields Included in All/Keywords | Required Roles (at least one) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research assets | All research assets, including research deposits | Research Assets | Keywords:
|
Research Assets Curator, Research Assets Manager, Esploro Observer |
| Research deposits | Research deposits only, not including approved research assets | Research Deposits | All:
|
Research Assets Curator, Research Assets Manager |
| Research files | Files associated with research assets and/or deposits | Research Files | Keywords – same fields as research assets | Research Assets Curator, Research Assets Manager, Esploro Observer |
| Researchers | Researchers and researcher proxies. The results for affiliated/non-affiliated researchers are presented in two separated tabs |
Find and Manage Researchers | All:
|
Researchers Manager |
|
Media Mentions |
Media Mentions | Media Mentions Manager | ||
| Projects | Projects | Keywords:
|
Project Curator, Project Manager |
The fields that you can search depend on the search type. For example, when you search research assets, the searchable fields include research asset fields such as title and author.
Performing a Simple Search
- Select the search type from the drop-down list. Only the search types relevant for your roles appear in the list.
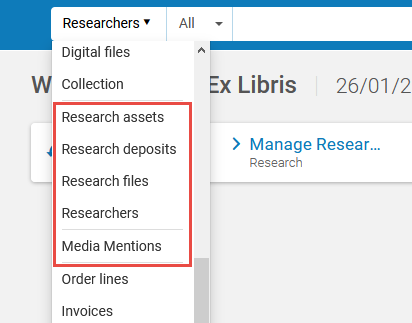 Persistent Search Drop-Down List of Search Types
Persistent Search Drop-Down List of Search Types - Select the field on which to search in the second drop-down list, or select Keywords or All (depending on the search type selected) for a general search on multiple fields. You can select the default field name and enter part or all of a field name to filter the list of fields.
- Enter a search string in the text box.
To jump to this text field on any page that does not have any other kind of search box, press / (forward slash) on your keyboard.Regarding the search string:
- Articles (such as the, a, an) in your search are ignored.
- All ISBNs are in ISBN-13 format.
- Special characters, such as hyphen, dash, slash, and so forth, are ignored. For additional special characters, see Searching for Special Characters.
- The asterisk ( * ) wildcard character may be used in your search string if the asterisk is placed at the end of the search string.
- Wildcards are not supported when the string contains a hyphen or dash, for example: stop-off.
- The question mark (?) is not supported as a wildcard character.
- Esploro finds characters with diacritics when you search using standard English characters.
If the users in your institution search using characters with diacritics, ensure that Ex Libris has configured that searches return matches for diacritics. Search language configuration is available for German, Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Korean, Chinese, and Hong Kong TSVCC.
- Contact Ex Libris to enable the following enhanced search options:
- Search in traditional Chinese/Kanji or simplified Chinese/Kanji and return results in both traditional Chinese/Kanji and simplified Chinese/Kanj.
- Search in Hangul (Korean) and return results in both Hangul and Hanja.
- Search in Hiragana (Japanese) and return results in both Hiragana and Katakana.
- Esploro saves the last 10 searches in search history for research asset searches. This list is saved indefinitely. There is currently no way to clear the list (other than to perform new searches).
- For the Open access search, enter one of the following search strings: Yes, No.
- Select the magnifying glass
 or press Return or Enter on the keyboard to perform the search. The items that match your search query appear on the page.
or press Return or Enter on the keyboard to perform the search. The items that match your search query appear on the page.
- For more information about the results, see:
- Research assets – Managing Research Assets
- Research deposits – Managing Research Deposits
- Research files – Research Files Search Results
- Researchers – Managing Researchers
- Media Mentions - Managing Media Mentions
- To save your search, see Rerunning, Saving, and Reusing Search Queries.
- For more information about the results, see:
Performing an Advanced Search
Currently, advanced search is only available for research assets. See Performing a Simple Search for information that applies to both simple and advanced searches.
- Select the search type from the drop-down list. Only the search types relevant for your roles appear in the list.
- Select Advanced to open the advanced search for this search type. The persistent search box expands to include the option to add additional rows of search criteria (additional fields and values).
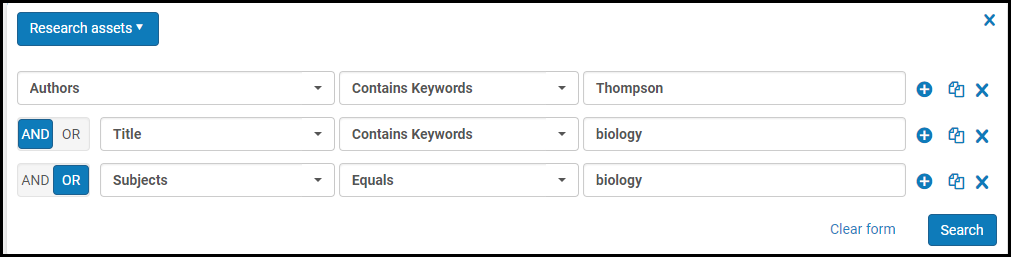 Advanced Search – Research Assets
Advanced Search – Research AssetsThe search starts with a single row. Each row contains a search field drop-down list, a comparison drop-down list, a search criteria text box/selection list, and action icons. For research assets, the fields are: Abstract, Additional dates, Asset ID/category/type, Author (also matches creators) name/ID/ORCID/affiliation, Conference, DOI, Electronic publication date, Format, Grant ID/name. ISBN/ISSN, Language, License name, Methods, Open access, Peer reviewed, Publication acceptance date/date/title, Publisher, Topics/Subjects, and Title.
- Currently there is a known issue when doing a Contains Keywords search where the value contains a period (.). In this case, Esploro matches the value if you search using: the complete value, a search term matching the start of the value up to the first period (with or without the first period), or a search that does not include a period. For example, if the value is aaa.bbb.ccc, searching for:
- aaa.bbb.ccc matches
- aaa bbb ccc matches (no periods in search)
- bbb matches (no periods in search)
- aaa. matches (matches the value up to and including the first period)
- aaa.bbb does not match (search includes a period but is not the full value)
- bbb.ccc does not match (search includes a period but is not the full value)
- When searching a date field, you must select/enter a complete date in the form dd/mm/yyyy. You cannot enter, for example, mm/yyyy or yyyy. The complete date matches all assets with that specific date or a more general partial date. For example, 29/01/2019 matches assets with 29/01/2019, 01/2019, and 2019, but not 28/01/2019.
- Advanced searches for assets based on the Date created field only look at the From date selected in the field. If a To date is also specified in the field, it is not included in the search.
- Currently there is a known issue when doing a Contains Keywords search where the value contains a period (.). In this case, Esploro matches the value if you search using: the complete value, a search term matching the start of the value up to the first period (with or without the first period), or a search that does not include a period. For example, if the value is aaa.bbb.ccc, searching for:
- To add additional rows, select the duplicate row icon
 or add row icon
or add row icon  . To remove a row (other than the first), select the delete row icon
. To remove a row (other than the first), select the delete row icon  . By default, each row represents additional search criteria that must also match (AND). Select OR in any row (other than the first) to change the combination type to OR. Implied parentheses are added around all search rows connected by ANDs.
. By default, each row represents additional search criteria that must also match (AND). Select OR in any row (other than the first) to change the combination type to OR. Implied parentheses are added around all search rows connected by ANDs. - Select the search field in the first drop-down (you can enter some text to filter the options).
- Select a comparison operator from the second drop-down. The list of comparisons depends on the field type.
- Enter the value in the last field in the row.
- Select Search or press Return on your keyboard. The results of an advanced search appear on the page, below the advanced search form. You can edit the advanced search and run a new search from the results page. Your current search logic appears at the top of the results, as in the following example.
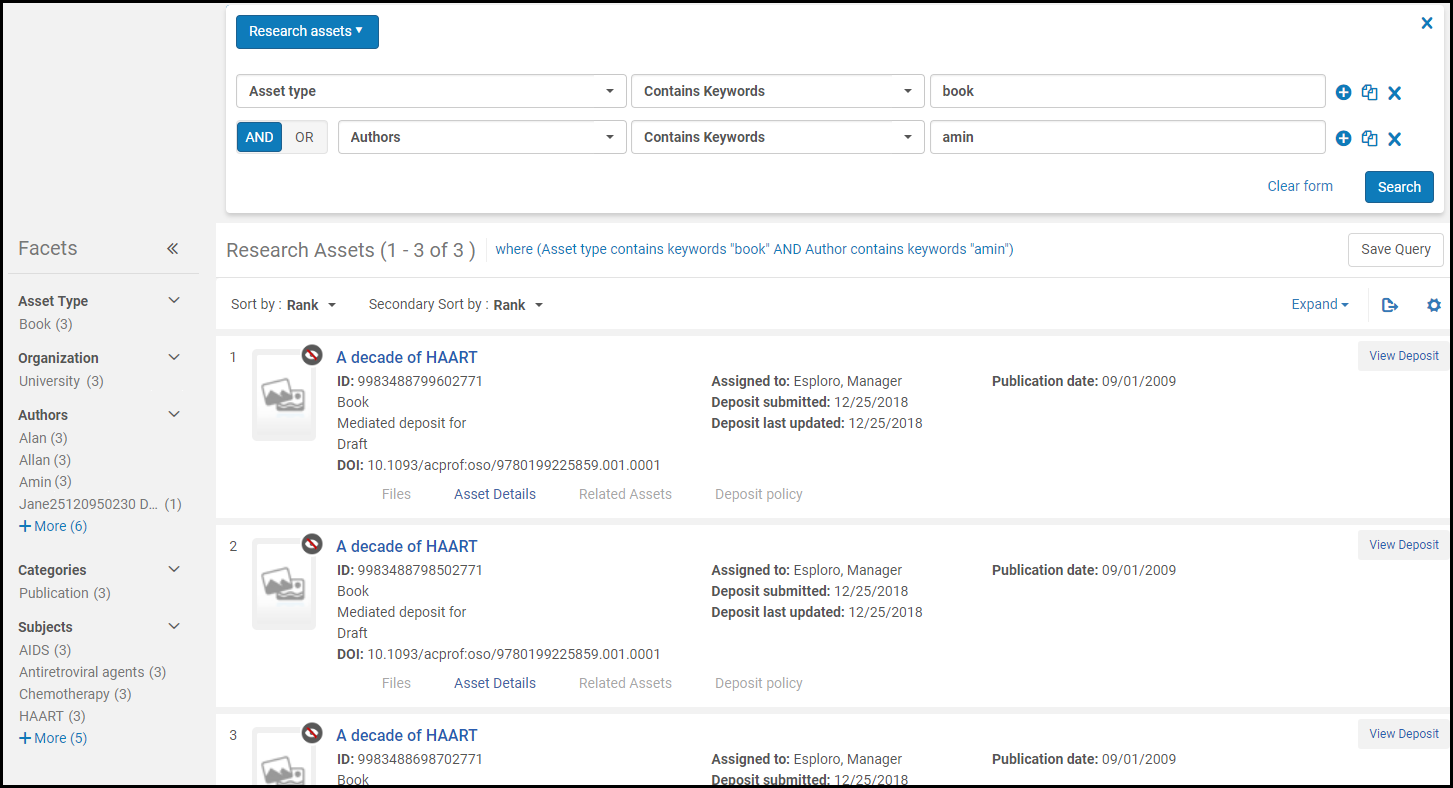 Advanced Search Results – Research Assets
Advanced Search Results – Research Assets
Rerunning, Saving, and Reusing Search Queries
- Research Asset Manager
To manage a researcher set, you must have the role:
- Researcher Manager
Any user can rerun one of his or her previous searches from the persistent search.
A manager can save searches for research assets for later use. A saved search query is another name for a logical set. A logical set is dynamic, recalculated each time it is accessed – in other words, the search is rerun and the results of the search are the set. When you save a query (set), you save the search criteria that can be reused. Each time you run a query, the results may be different if the records have changed since the previous run. In contrast, an itemized set is a fixed collection of items that you enter by hand, upload from a file, or save as a specific set of items: they may be the result of a previous search, but the set is no longer associated with the query. Note that you can turn logical sets into itemized sets.
For more information about sets, see Managing Search Queries and Sets.
Select the text box and select a previous search from the drop-down list that appears. The search runs immediately. When no recent searches appear, you may be able to select a previous search string using your browser history. You can also rerun a previously saved search for research assets (see Rerunning, Saving, and Reusing Search Queries).
- After performing a search, select Save Query on the search results.
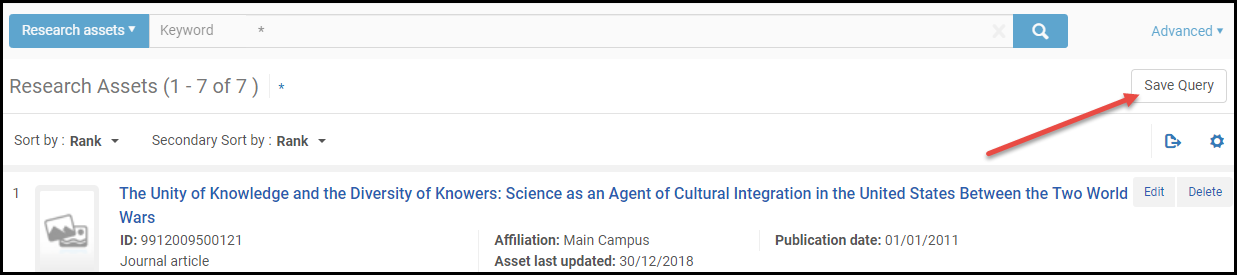 Save Query ButtonThe Set Details page appears.
Save Query ButtonThe Set Details page appears.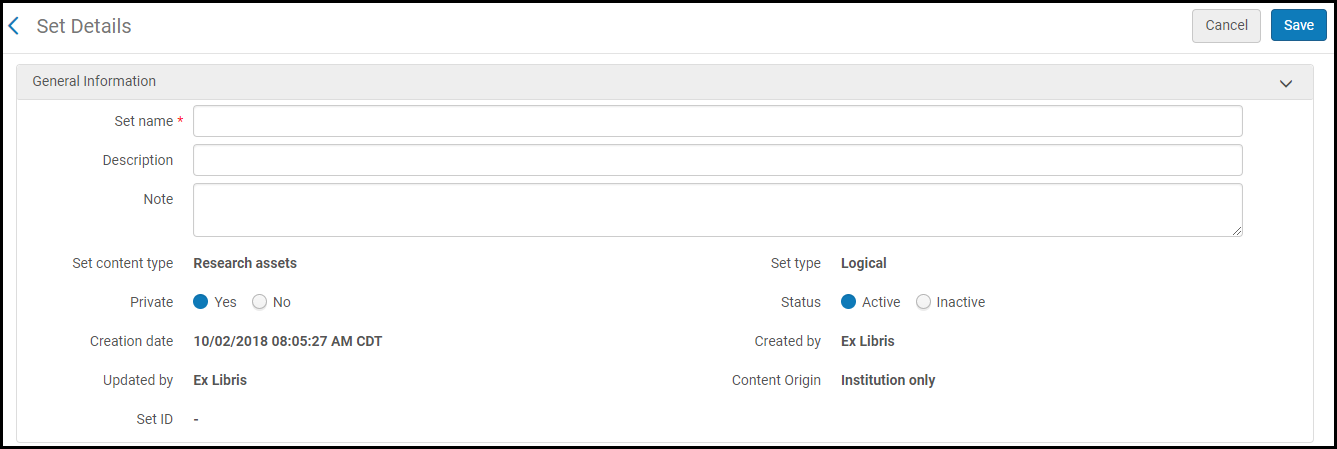 Set Details Page
Set Details Page - Follow the procedure in Creating Logical Sets.
Alternately, you can also create an itemized set of research assets on the Manage Sets page; see Creating Itemized Sets.
You can create a logical set of researchers on the Manage Sets page. Follow the procedure in Creating Logical Sets. You can also create an itemized set of researchers on this page.
On the Manage Sets page (Admin > Manage Jobs and Sets > Manage Sets), locate the saved query (logical set) and select Results in the row actions list. For more information, see Managing Search Queries and Sets.
Research Files Search Results
Search results for research asset files appear in a record list. The results appear similar to the results of a research assets search, with different fields appearing for each record, such as file title, file extension, and PID. You can configure the fields and actions that appear for each result; for more information see Record Lists.
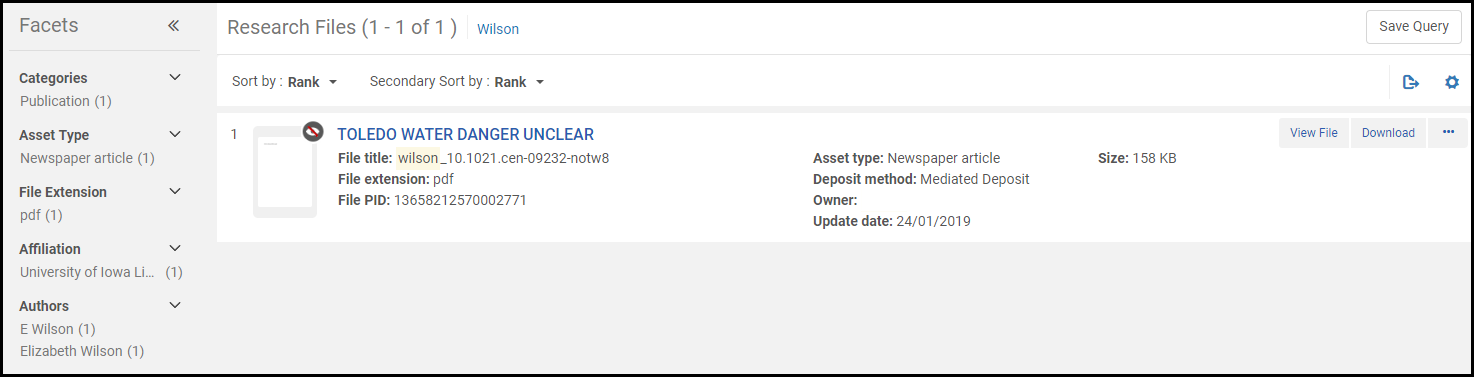
The file PID is a unique ID that can be used to search for this file at a later time. For all other information about sorting, filtering, icons, and the asset viewer, see Managing Research Assets.
The actions on this page include:
- View File/s
- Download
- Edit – Edit the asset to which this file is associated.
Exporting Citations
For a video showing how to export citations see here.
To export citations from asset search results, select Export Citations.
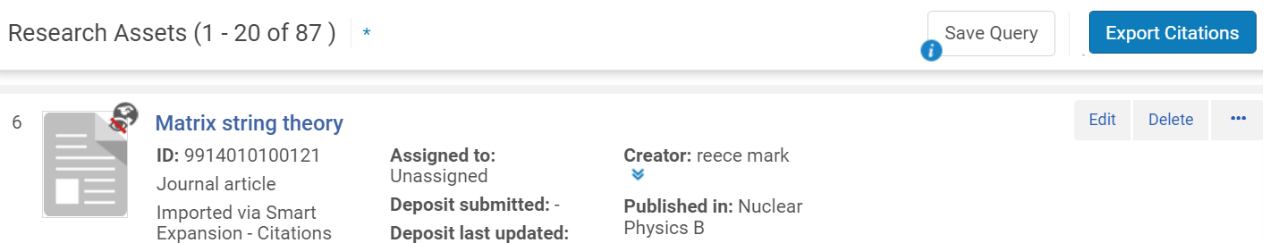
After exporting, an email is sent with the list of citations to the email address set in the Citation style window.
You configure citation export from Configuration > General > Citations Format.

Searching for Special Characters
German Characters
| German Language Character/Character Combinations | Stored in the Esploro Database |
|---|---|
| ß | ss |
| ä, Ä | ae |
| ö, Ö | oe |
| ü, Ü | ue |
| ae | ae |
| oe | oe |
| ue (when not following a vowel or q) | ue |
Spanish and Catalan Characters
| Letter | Search | Sort |
|---|---|---|
| Ñ/ñ | Searching for Ñ/ñ does not retrieve results for N/n and vice versa. | Sorted after n. |
| Ç/ç | Searching for Ç/ç does not retrieve results of C/c and vice versa. | Sorted after c. |
| L·L/l·l | Searched for as if it were the digraph ll. | Sorted as ll. |
- Without diacritics
- Acute
- Grave
- Dieresis
Scandinavian Characters
| Norwegian and Danish Sorting |
|---|
| ... |
| Ad/ad
Ae/ae
Af/af
|
| ... |
| Od/od
Oe /oe
Of/of
|
| ... |
| Ud/ud
Ue/ue
Uf/uf
|
| ... |
| X/x
Y/y + Ü/ü (except for tremas like Leüs)
Z/z
Æ/æ + Ä/ä
Ø/ø + Ö/ö
Å/å + Aa/aa
|
| Swedish Sorting |
|---|
| ... |
| Ad/ad
Ae/ae + Æ/æ
Af/af
|
| ... |
| Od/od
Oe /oe
Of/of
|
| ... |
| Ud/ud
Ue/ue
Uf/uf
|
| ... |
| X/x
Y/y + Ü/ü
Z/z
Å/å
Ä/ä
Ö/ö + Ø/ø
|
Chinese and Korean Characters
Japanese Characters
- Punctuation removal
- Normalization between Hiragana and Katakana
- Iterated character normalization
- Normalization of variant Kanji characters
CJK Punctuation
Hong Kong TSVCC
- Searching metadata records
- Searching for Chinese user names
Polish Characters
| Uppercase | Lowercase | Diacritics |
|---|---|---|
| A | a | |
| Ą | ą | ogonek |
| B | b | |
| C | c | |
| Ć | ć | acute |
| D | d | |
| E | e | |
| Ę | ę | ogonek |
| F | f | |
| G | g | |
| H | h | |
| I | i | |
| J | j | |
| K | k | |
| L | l | |
| Ł | ł | stroke |
| M | m | |
| N | n | |
| Ń | ń | acute |
| O | o | |
| Ó | ó | acute |
| P | p | |
| Q | q | |
| R | r | |
| S | s | |
| Ś | ś | acute |
| T | t | |
| U | u | |
| V | v | |
| W | w | |
| X | x | |
| Y | y | |
| Z | z | |
| Ź | ź | acute |
| Ż | ż |
dot |
Czech Characters
| Uppercase | Lowercase | Diacritics |
|---|---|---|
| A | a | |
| Á | á | acute |
| B | B | |
| C | c | |
| Č | č | caron |
| D | d | |
| Ď | ď | acute |
| E | e | |
| É | é | acute |
| Ě | ě | caron |
| F | f | |
| G | g | |
| H | h | |
| Ch | ch | |
| I | i | |
| Í | í | acute |
| J | j | |
| K | k | |
| L | l | |
| M | m | |
| N | n | |
| Ň | ň | caron |
| O | o | |
| Ó | ó | acute |
| P | p | |
| Q | q | |
| R | r | |
| Ř | ř | caron |
| S | s | |
| Š | š | caron |
| T | t | |
| Ť | ť | acute |
| U | u | |
| Ú | ú | acute |
| Ů | ů | ring |
| V | v | |
| W | w | |
| X | x | |
| Y | y | |
| Ý | ý | acute |
| Z | z | |
| Ž | ž | caron |

